Kafka源码01(Producer)
导入代码
idea导入 -> idea自动处理 gradle
https://github.com/apache/kafka
Kafka 版本 2.11-2.4.0 切换到 2.4 分支
Producer 数据发送流程
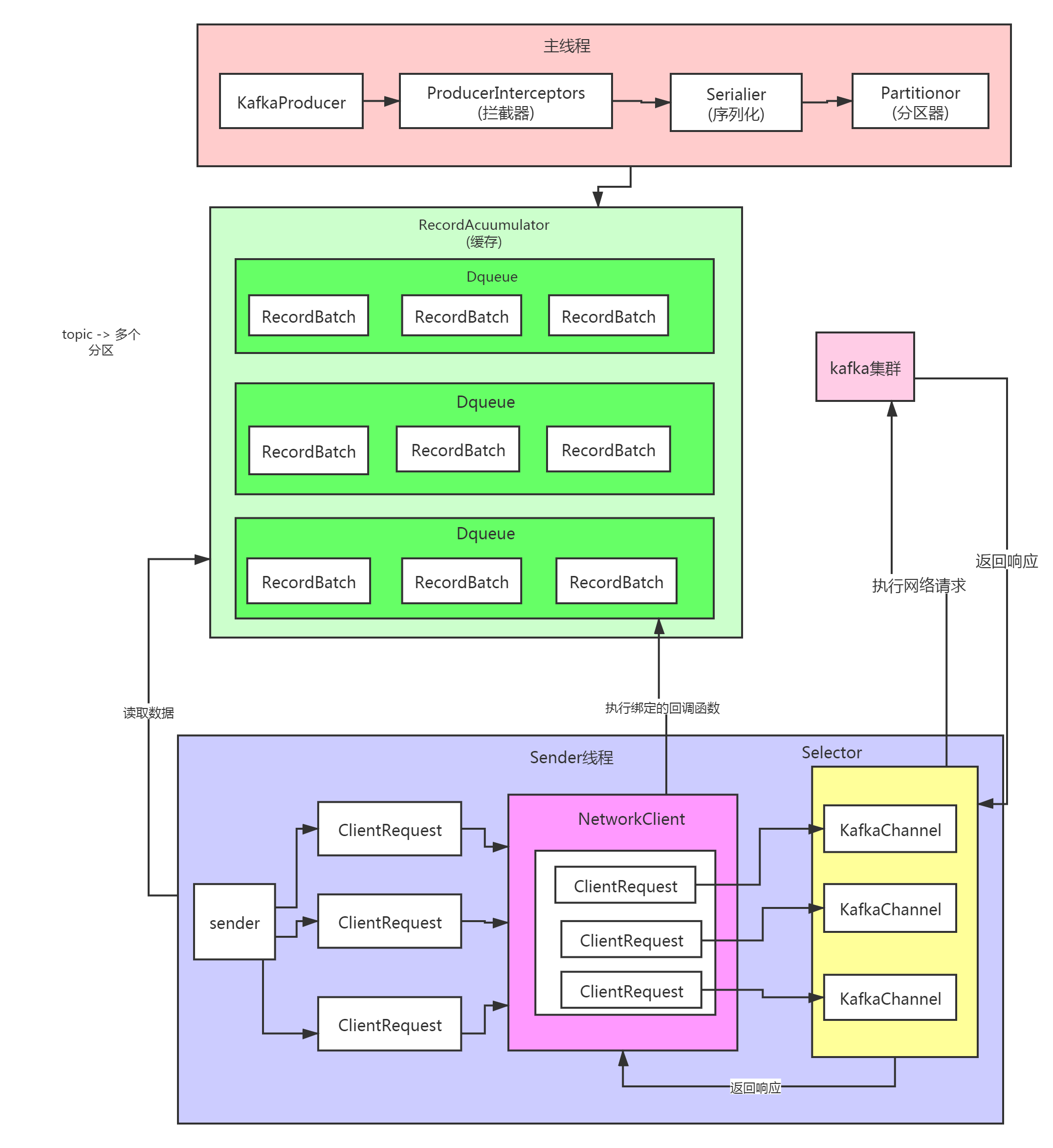

- 获取topic的metadata
- Serialzer对key和value进行序列化
- Partitioner对消息选择合适的分区
- RecordAccumulator追加record数据消息,实现批量发送
- Sender从RecordAccumulator获取消息,batch满了唤醒sender线程发送数据。
- 构造ClientRequest
- 将ClientRequest交给Network,准备发送
- Network将请求放入KafkaChannel的缓存
- 发送请求
- 收到响应
- 调用RecordBatch的回调函数,最终调用到每一个消息上注册的回调函数
主线程主要负责封装消息成ProducerRecord对象,之后调用send方法将消息放入RecordAccumulator中暂存。Sender线程负责将消息构造成请求,并从RecordAccumulator取出消息消息并批量发送。
public class Producer extends Thread {
private final KafkaProducer<Integer, String> producer;
private final String topic;
private final Boolean isAsync;
public Producer(String topic, Boolean isAsync) {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, KafkaProperties.KAFKA_SERVER_URL + ":" + KafkaProperties.KAFKA_SERVER_PORT);
props.put(ProducerConfig.CLIENT_ID_CONFIG, "DemoProducer");
props.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, IntegerSerializer.class.getName());
props.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName());
producer = new KafkaProducer<>(props);
this.topic = topic;
this.isAsync = isAsync;
}
public void run() {
int messageNo = 1;
while (true) {
String messageStr = "Message_" + messageNo;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (isAsync) {
// 异步发送,一直发送,消息响应结果交给回调函数处理
producer.send(new ProducerRecord<>(topic,
messageNo,
messageStr), new DemoCallBack(startTime, messageNo, messageStr));
} else {
// 同步发送
try {
producer.send(new ProducerRecord<>(topic,
messageNo,
messageStr)).get();
System.out.println("Sent message: (" + messageNo + ", " + messageStr + ")");
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
++messageNo;
}
}
}
同步,用send返回Future时,需要立即调用get,因为Future在没有返回结果时会一直阻塞
异步,提供一个回调,调用send后可以继续发送消息,不用等待。当有结果返回时,会自动执行回调函数。
// 实现Callback接口,并用Future接收线程的执行结果
public Future<RecordMetadata> send(ProducerRecord<K, V> record) {
return send(record, null);
}
public Future<RecordMetadata> send(ProducerRecord<K, V> record, Callback callback) {
ProducerRecord<K, V> interceptedRecord = this.interceptors.onSend(record);
return doSend(interceptedRecord, callback);
}
获取topic的metadata
topics 用 hashMap 存储,topic -> 过期时间。Producer 调用 dosend() 方法,通过 waitOnMetadata 方法获取该 topic 的 metadata 信息。如果 metadata 中不存在这个 topic 的 metadata,那么就请求更新 metadata,如果 metadata 没有更新的话,方法就一直处在 do … while 的循环之中。若超时抛出异常。
- 主线程发送消息
- waitOnMetadata方法,topics不存在topic
- metadata.requestUpdateForNewTopics() 将 metadata 的 needUpdate 变量设置为 true,触发强制更新,并返回updateVersion,通过版本号来判断 metadata 是否完成更新。
- sender.wakeup() 唤醒 sender 线程,Sendsenderer再唤醒NetworkClient,通知客户端开始服务,client也唤醒Selector,最终唤醒
NIO的Selector; - metadata.awaitUpdate(version, remainingWaitMs) 是通过比较版本号的方式,控制数据一致性。在Metadata.awaitUpdate() 方法中,线程会阻塞在 while 循环中,直到metadata更新成功或者timeout。这里需要注意,metadata中的字段可以有主线程读、sender线程更新,也是通过wait/notify同步机制做到。它加上synchronized 是线程安全的。
- networkClient的poll方法继续运行,selector的poll方法通过复杂网络操作将请求发给集群。服务端返回响应,对selector的completedReceives(服务端返回的数据)进行处理
- 更新本地元数据缓存
- 唤醒主线程

metadata 是如何更新的呢?
通过 sender.wakeup() 来唤醒 sender 线程,间接唤醒 NetworkClient 线程,NetworkClient 线程来负责发送 Metadata 请求,并处理 Server 端的响应。
sender.java
/**
* Wake up the selector associated with this send thread
*/
public void wakeup() {
this.client.wakeup();
}
NetworkClient.java
/**
* Interrupt the client if it is blocked waiting on I/O.
*/
@Override
public void wakeup() {
this.selector.wakeup();
}
/**
* Interrupt the nioSelector if it is blocked waiting to do I/O.
*/
@Override
public void wakeup() {
this.nioSelector.wakeup();
}
Producer Metadata 的更新策略
- KafkaProducer 第一次发送消息时强制更新,其他时间周期性更新
- 强制更新: 调用 Metadata.requestUpdate() 将 needUpdate 置成了 true 来强制更新。
Metadata 的强制更新会在以下几种情况下进行,强制更新主要是用于处理各种异常情况。
- initConnect 方法调用时,初始化连接;
- poll() 方法中对 handleDisconnections() 方法调用来处理连接断开的情况,这时会触发强制更新;
- poll() 方法中对 handleTimedOutRequests() 来处理请求超时时;
- 发送消息时,如果无法找到 partition 的 leader;
- 处理 Producer 响应(handleProduceResponse),如果返回关于 Metadata 过期的异常,比如:没有 topic-partition 的相关 meta 或者 client 没有权限获取其 metadata。
Metadata 内容。
// Metadata 封装了cluster对象、listener监听器。并保存cluster数据的最后更新日期、版本号、是否需要更新等待信息。
public class Metadata implements Closeable {
private final Logger log;
private final long refreshBackoffMs; // metadata 更新失败时为避免频繁更新 meta,减少网络的压力,最小的间隔时间,默认 100ms
private final long metadataExpireMs; // metadata 的过期时间
private int updateVersion; // bumped on every metadata response 每更新成功1次,version自增1,主要是用于判断 metadata 是否更新
private int requestVersion; // bumped on every new topic addition 每更新一次,判断是否同一次更新
private long lastRefreshMs; // 最近一次更新时的时间(包含更新失败的情况)
private long lastSuccessfulRefreshMs; // 最近一次成功更新的时间(如果每次都成功的话,与前面的值相等, 否则,lastSuccessulRefreshMs < lastRefreshMs)
private KafkaException fatalException;
private Set<String> invalidTopics;
private Set<String> unauthorizedTopics;
private MetadataCache cache = MetadataCache.empty();
private boolean needUpdate; // 是都需要更新 metadata
private final ClusterResourceListeners clusterResourceListeners;
private boolean isClosed;
private final Map<TopicPartition, Integer> lastSeenLeaderEpochs;
}
public class ProducerMetadata extends Metadata {
private static final long TOPIC_EXPIRY_NEEDS_UPDATE = -1L;
static final long TOPIC_EXPIRY_MS = 5 * 60 * 1000; // TOPIC 过期时间5分钟
}
public final class Cluster {
private final boolean isBootstrapConfigured;
private final List<Node> nodes; // node 列表
private final Set<String> unauthorizedTopics; // 未认证的 topic 列表
private final Set<String> invalidTopics;
private final Set<String> internalTopics; // 内置的 topic 列表
private final Node controller;
private final Map<TopicPartition, PartitionInfo> partitionsByTopicPartition; // partition 的详细信息
private final Map<String, List<PartitionInfo>> partitionsByTopic; // topic 与 partition 的对应关系
private final Map<String, List<PartitionInfo>> availablePartitionsByTopic; // 可用(leader 不为 null)的 topic 与 partition 的对应关系
private final Map<Integer, List<PartitionInfo>> partitionsByNode; // node 与 partition 的对应关系
private final Map<Integer, Node> nodesById; // node 与 id 的对应关系
private final ClusterResource clusterResource;
}
// TopicPartition Topic 分区
public final class TopicPartition implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -613627415771699627L;
private int hash = 0;
private final int partition;
private final String topic;
public TopicPartition(String topic, int partition) {
this.partition = partition;
this.topic = topic;
}
}
// PartitionInfo: 分区详细信息,包含 topic、partition、leader、replicas、isr
public class PartitionInfo {
private final String topic;
private final int partition;
private final Node leader;
private final Node[] replicas;
private final Node[] inSyncReplicas;
private final Node[] offlineReplicas;
}
// Node Kafka节点信息
public class Node {
private static final Node NO_NODE = new Node(-1, "", -1);
private final int id; // 节点id
private final String idString;
private final String host; // 主机
private final int port; // 端口 默认 9092
private final String rack; // 机架
}
topic describe
Topic:test01 PartitionCount:2 ReplicationFactor:3 Configs:
Topic: test01 Partition: 0 Leader: 82 Replicas: 82,83,81 Isr: 83,82,81
Topic: test01 Partition: 1 Leader: 83 Replicas: 83,81,82 Isr: 83,82,81
调用KafkaClient.poll的方法。具体实现就是KafkaClient的子类NetworkClient
public List<ClientResponse> poll(long timeout, long now) {
ensureActive();
if (!abortedSends.isEmpty()) {
// If there are aborted sends because of unsupported version exceptions or disconnects,
// handle them immediately without waiting for Selector#poll.
List<ClientResponse> responses = new ArrayList<>();
handleAbortedSends(responses);
completeResponses(responses);
return responses;
}
// 封装了一个要拉取元数据请求
long metadataTimeout = metadataUpdater.maybeUpdate(now);
try {
// 执行网络IO的操作 NIO
this.selector.poll(Utils.min(timeout, metadataTimeout, defaultRequestTimeoutMs));
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("Unexpected error during I/O", e);
}
// process completed actions
long updatedNow = this.time.milliseconds();
List<ClientResponse> responses = new ArrayList<>();
handleCompletedSends(responses, updatedNow);
handleCompletedReceives(responses, updatedNow);
handleDisconnections(responses, updatedNow);
handleConnections();
handleInitiateApiVersionRequests(updatedNow);
handleTimedOutRequests(responses, updatedNow);
completeResponses(responses);
return responses;
}
metadataUpdater.maybeUpdate(now):判断是否需要更新 Metadata,如果需要更新的话,先与 Broker 建立连接,然后发送更新 metadata 的请求;
metadataUpdater.handleSuccessfulResponse(req.header, now, (MetadataResponse) body);
public void handleSuccessfulResponse(RequestHeader requestHeader, long now, MetadataResponse response) {
List<TopicPartition> missingListenerPartitions = response.topicMetadata().stream().flatMap(topicMetadata ->
topicMetadata.partitionMetadata().stream()
.filter(partitionMetadata -> partitionMetadata.error() == Errors.LISTENER_NOT_FOUND)
.map(partitionMetadata -> new TopicPartition(topicMetadata.topic(), partitionMetadata.partition())))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
if (response.brokers().isEmpty()) {
this.metadata.failedUpdate(now);
} else {
this.metadata.update(inProgressRequestVersion, response, now);
}
inProgressRequestVersion = null;
}
updateVersion + 1
handleCompletedReceives(responses, updatedNow) 方法,它会处理 Server 端返回的 Metadata 结果。
class DefaultMetadataUpdater implements MetadataUpdater {
public long maybeUpdate(long now) {
// should we update our metadata?
// metadata 下次更新的时间(需要判断是强制更新还是 metadata 过期更新,前者是立即更新,后者是计算 metadata 的过期时间)
long timeToNextMetadataUpdate = metadata.timeToNextUpdate(now);
// 是否发送了metadataRequest请求 ,那么时间设置为 waitForMetadataFetch(默认30s)
long waitForMetadataFetch = hasFetchInProgress() ? defaultRequestTimeoutMs : 0;
// 计算当前距离下次可以发送metadataRequest请求的时间
long metadataTimeout = Math.max(timeToNextMetadataUpdate, waitForMetadataFetch);
if (metadataTimeout > 0) {
return metadataTimeout;
}
// Beware that the behavior of this method and the computation of timeouts for poll() are
// highly dependent on the behavior of leastLoadedNode.
// 找到负载最小的node,若没有可用的node,则返回null
Node node = leastLoadedNode(now);
if (node == null) {
log.debug("Give up sending metadata request since no node is available");
return reconnectBackoffMs;
}
return maybeUpdate(now, node);
}
private long maybeUpdate(long now, Node node) {
String nodeConnectionId = node.idString();
if (canSendRequest(nodeConnectionId, now)) {
Metadata.MetadataRequestAndVersion requestAndVersion = metadata.newMetadataRequestAndVersion();
MetadataRequest.Builder metadataRequest = requestAndVersion.requestBuilder;
log.debug("Sending metadata request {} to node {}", metadataRequest, node);
sendInternalMetadataRequest(metadataRequest, nodeConnectionId, now);
this.inProgressRequestVersion = requestAndVersion.requestVersion;
return defaultRequestTimeoutMs;
}
}
}
Serialzer对key和value进行序列化
消息必须序列化为二进制流的形式才能在网络中传输
Partitioner对消息选择合适的分区
选择分区,表示消息要存储到Kafka集群的哪个节点上。生产者可以将一批消息分成多个分区,每个分区写入不同的服务端节点,不同的分区可以同时向分区leader副本节点写入数据,使用分区并行发送的方式,提高客户端的写入性能。
record有传partition,则使用,没有就按配置的partitioner class计算partition。
- keyBytes不为null,hash keyBytes,再与分区数量取模运算,选择partition
- keyBytes为null,使用黏性分区策略(StickyPartitioning Strategy),解决了将没有键的记录分散成较小批次的问题。(kafka 2.4版本之前为轮询,round-robin的方式)
RecordAccumulator追加record数据消息
将消息先缓存到客户端的记录收集器,等待满足条件再发送线程Sender批量写入Kafka集群。生产者每生产一条消息(默认最大1M),就向记录收集器中追加一条消息。追加方法的返回值表示批记录(RecordBatch)是否满了,如果批记录满了,则开始发送这一批数据。

private Future<RecordMetadata> doSend(ProducerRecord<K, V> record, Callback callback) {
...
int partition = partition(record, serializedKey, serializedValue, cluster);
tp = new TopicPartition(record.topic(), partition);
//设置消息头只读
setReadOnly(record.headers());
Header[] headers = record.headers().toArray();
// 估算消息大小
int serializedSize = AbstractRecords.estimateSizeInBytesUpperBound(apiVersions.maxUsableProduceMagic(),
compressionType, serializedKey, serializedValue, headers);
// 检查大小不超过maxRequestSize(默认1M)和totalMemorySize(默认32M)
ensureValidRecordSize(serializedSize);
// 获取消息的时间
long timestamp = record.timestamp() == null ? time.milliseconds() : record.timestamp();
...
// producer callback will make sure to call both 'callback' and interceptor callback
// 异步方式发送的消息给每一条消息都绑定回调函数。
Callback interceptCallback = new InterceptorCallback<>(callback, this.interceptors, tp);
if (transactionManager != null && transactionManager.isTransactional()) {
transactionManager.failIfNotReadyForSend();
}
// 追加数据到记录收集器(32M的内存),accumulator把消息封装成为一个批次一个批次的去发送
RecordAccumulator.RecordAppendResult result = accumulator.append(tp, timestamp, serializedKey,
serializedValue, headers, interceptCallback, remainingWaitMs, true);
if (result.batchIsFull || result.newBatchCreated) {
// 唤醒sender线程。真正发送数据的线程
this.sender.wakeup();
}
...
}
RecordAccumulator
public final class RecordAccumulator {
private final BufferPool free;
// batches是concurrentMap实现类,k 是topic+partiton封装的类, v是队列。在getOrCreateDeque方法中,如果batches没有tp,那就新建一个队列并返回。
private final ConcurrentMap<TopicPartition, Deque<ProducerBatch>> batches;
// batches CopyOnWriteMap
public RecordAccumulator(...) {
this.batches = new CopyOnWriteMap<>();
this.free = bufferPool;
}
// CopyOnWrite 读写分离
private Deque<ProducerBatch> getOrCreateDeque(TopicPartition tp) {
Deque<ProducerBatch> d = this.batches.get(tp);
if (d != null)
return d;
d = new ArrayDeque<>();
Deque<ProducerBatch> previous = this.batches.putIfAbsent(tp, d);
if (previous == null)
return d;
else
return previous;
}
public RecordAppendResult append(TopicPartition tp,
long timestamp,
byte[] key,
byte[] value,
Header[] headers,
Callback callback,
long maxTimeToBlock,
boolean abortOnNewBatch) throws InterruptedException {
// We keep track of the number of appending thread to make sure we do not miss batches in
// abortIncompleteBatches().
appendsInProgress.incrementAndGet();
ByteBuffer buffer = null;
if (headers == null) headers = Record.EMPTY_HEADERS;
try {
// 如果batches没有tp,那就新建一个队列并返回。
// check if we have an in-progress batch
Deque<ProducerBatch> dq = getOrCreateDeque(tp);
// 锁住这个队列,只能有一个send线程获得dq对象,往里面tryAppend
synchronized (dq) {
if (closed)
throw new KafkaException("Producer closed while send in progress");
// tryAppend,取deque最后一个元素,如果有,那就试着加进去(有可能因为size问题或者根本没有元素不成功),返回的future就是空的。
RecordAppendResult appendResult = tryAppend(timestamp, key, value, headers, callback, dq);
if (appendResult != null)
return appendResult;
}
// we don't have an in-progress record batch try to allocate a new batch
if (abortOnNewBatch) {
// Return a result that will cause another call to append.
return new RecordAppendResult(null, false, false, true);
}
// 估计消息大小,给内存分配计算,取batchSize和消息最大值
byte maxUsableMagic = apiVersions.maxUsableProduceMagic();
int size = Math.max(this.batchSize, AbstractRecords.estimateSizeInBytesUpperBound(maxUsableMagic, compression, key, value, headers));
log.trace("Allocating a new {} byte message buffer for topic {} partition {}", size, tp.topic(), tp.partition());
buffer = free.allocate(size, maxTimeToBlock);
// 分配好内存,又锁住dq,再一次tryAppend,目的避免内存碎片的出现
synchronized (dq) {
// Need to check if producer is closed again after grabbing the dequeue lock.
if (closed)
throw new KafkaException("Producer closed while send in progress");
RecordAppendResult appendResult = tryAppend(timestamp, key, value, headers, callback, dq);
if (appendResult != null) {
// Somebody else found us a batch, return the one we waited for! Hopefully this doesn't happen often...
return appendResult;
}
// 新建估算大小的recordsBuilder,封装进batch,batch装消息
MemoryRecordsBuilder recordsBuilder = recordsBuilder(buffer, maxUsableMagic);
ProducerBatch batch = new ProducerBatch(tp, recordsBuilder, time.milliseconds());
FutureRecordMetadata future = Objects.requireNonNull(batch.tryAppend(timestamp, key, value, headers,
callback, time.milliseconds()));
// dq装batch
dq.addLast(batch);
incomplete.add(batch);
// Don't deallocate this buffer in the finally block as it's being used in the record batch
buffer = null;
return new RecordAppendResult(future, dq.size() > 1 || batch.isFull(), true, false);
}
} finally {
if (buffer != null)
free.deallocate(buffer);
appendsInProgress.decrementAndGet();
}
}
}
为什么分多个synchronized块而不是一个完整的synchronized块中完成?
目的:提升吞吐量
因为向BufferPool申请新ByteBuffer的时候,可能会导致阻塞。我们假设在一个synchronized块中完成所有的追加操作。假设场景:线程1发送的消息比较大,需要向BufferPool申请新的空间,而此时BufferPool空间不足,线程1在BufferPool上等待,此时线程1依然持有相应的Deque的锁;线程2发送的消息较小,Deque最后一个RecordBatch剩余空间够用,但是线程1没释放Deque的锁,线程2也要等待,如果类似线程2的线程很多,就造成很多不必要的线程阻塞,降低了吞吐量。这里体现了“减少锁的持有时间”的优化手段。
读写分离
batches CopyOnWriteMap
实现的ConcurrentMap方法,用读写分离来实现线程安全,多个线程在读取这个map时候,会得到这个指向这个map的指针。如果有线程想修改map内容,系统就复制一份map,在这个线程修改好以后,把新的指针赋给ConcurrentMap实现类。可以看到下面的put方法是 synchronized修饰的,因此同一时间只能有一个线程修改内容。在修改的时候别的线程依然可以用老的指针读取。这个非常适合读多写少的场景。
public class CopyOnWriteMap<K, V> implements ConcurrentMap<K, V> {
public synchronized V put(K k, V v) {
Map<K, V> copy = new HashMap<K, V>(this.map);
V prev = copy.put(k, v);
this.map = Collections.unmodifiableMap(copy);
return prev;
}
public synchronized V putIfAbsent(K k, V v) {
if (!containsKey(k))
return put(k, v);
else
return get(k);
}
}

内存池设计
Kafka 封装了一个内存结构,把每个分区的消息封装成批次,缓存到内存里。反复利用每一个批次,减少Java虚拟机的内存回收。
maxRequestSize -> max.request.size(单个消息最大默认1M)
totalMemorySize -> buffer.memory(内存默认最大32M)
每个 recordBatch 的大小(16K)


Kafka生产者用内存池来循环利用中间生成的消息缓存bytebuffer。标准大小消息的bytebuffer,用过一次后接着用装下一条消息。对于非标准大小的消息,用另外手段分配。
RecordAccumulator中的append方法是把消息添加进batches里面的相应dqueue,在添加前需要把消息放进bytebuffer里面,bytebuffer从free里面allocate方法要来的。多个生产者会有线程安全问题,比如这边计算可用内存后别人给用掉了,所以allocate时候要锁住Bufferpool。
BufferPool负责ByteBuffer的申请和释放。 BufferPool会维持一组大小为poolableSize的ByteBuffer,便于快速申请/归还这个大小的ByteBuffer。该机制是由free空闲链表维持的。 对于非poolableSize的ByteBuffer,其申请和释放都委托给JVM。
buffer = free.allocate(size, maxTimeToBlock);
public class BufferPool {
//总大小 默认32M
private final long totalMemory;
//标准批次大小(由batch.size配置,默认16k)
private final int poolableSize;
//可用bytebuffer
private final Deque<ByteBuffer> free;
//因为内存不足等待的线程队列
private final Deque<Condition> waiters;
//totalMemory - poolableSize*free.size() - 使用中的butebuffer总大小
private long nonPooledAvailableMemory;
}
public ByteBuffer allocate(int size, long maxTimeToBlockMs) throws InterruptedException {
if (size > this.totalMemory)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Attempt to allocate " + size
+ " bytes, but there is a hard limit of "
+ this.totalMemory
+ " on memory allocations.");
ByteBuffer buffer = null;
this.lock.lock();
if (this.closed) {
this.lock.unlock();
throw new KafkaException("Producer closed while allocating memory");
}
try {
// 1. free队列有bytebuffer且size是标准大小,直接安排覆写bytebuffer
// check if we have a free buffer of the right size pooled
if (size == poolableSize && !this.free.isEmpty())
return this.free.pollFirst();
// 2. size大于标准且可用内存能满足size,走 safeAllocateByteBuffer(size),找一块内存安排上(这块内存就无法回收到free队列了,只能靠JVM回收),同时nonPooledAvailableMemory扣减size大小
// now check if the request is immediately satisfiable with the
// memory on hand or if we need to block
int freeListSize = freeSize() * this.poolableSize;
if (this.nonPooledAvailableMemory + freeListSize >= size) {
// we have enough unallocated or pooled memory to immediately
// satisfy the request, but need to allocate the buffer
freeUp(size);
this.nonPooledAvailableMemory -= size;
} else {
// 3. size大于标准但可用内存不能满足size或size大于标准但是free空了,等待在使用的bytebuffer释放
// we are out of memory and will have to block
int accumulated = 0;
// 关于 Condition,依赖lock,条件队列,加锁,等待信号
Condition moreMemory = this.lock.newCondition();
try {
long remainingTimeToBlockNs = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toNanos(maxTimeToBlockMs);
this.waiters.addLast(moreMemory);
// loop over and over until we have a buffer or have reserved
// enough memory to allocate one
// 循环等待至有足够空间进行分配
while (accumulated < size) {
long startWaitNs = time.nanoseconds();
long timeNs;
boolean waitingTimeElapsed;
try {
waitingTimeElapsed = !moreMemory.await(remainingTimeToBlockNs, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
} finally {
long endWaitNs = time.nanoseconds();
timeNs = Math.max(0L, endWaitNs - startWaitNs);
recordWaitTime(timeNs);
}
if (this.closed)
throw new KafkaException("Producer closed while allocating memory");
if (waitingTimeElapsed) {
throw new TimeoutException("Failed to allocate memory within the configured max blocking time " + maxTimeToBlockMs + " ms.");
}
remainingTimeToBlockNs -= timeNs;
// check if we can satisfy this request from the free list,
// otherwise allocate memory
if (accumulated == 0 && size == this.poolableSize && !this.free.isEmpty()) {
// just grab a buffer from the free list
buffer = this.free.pollFirst();
accumulated = size;
} else {
// we'll need to allocate memory, but we may only get
// part of what we need on this iteration
freeUp(size - accumulated);
int got = (int) Math.min(size - accumulated, this.nonPooledAvailableMemory);
this.nonPooledAvailableMemory -= got;
accumulated += got;
}
}
// Don't reclaim memory on throwable since nothing was thrown
accumulated = 0;
} finally {
// 循环过程中失败,则退还累计分配的空间
// When this loop was not able to successfully terminate don't loose available memory
this.nonPooledAvailableMemory += accumulated;
this.waiters.remove(moreMemory);
}
}
} finally {
// signal any additional waiters if there is more memory left
// over for them
// 还有空闲空间,就唤醒下一个线程
try {
if (!(this.nonPooledAvailableMemory == 0 && this.free.isEmpty()) && !this.waiters.isEmpty())
this.waiters.peekFirst().signal();
} finally {
// Another finally... otherwise find bugs complains
lock.unlock();
}
}
if (buffer == null)
// 进行非池化页空间的实际分配
return safeAllocateByteBuffer(size);
else
return buffer;
}
}
batch满了唤醒sender线程发送数据
发送消息的流程图

发送消息的工作统一由Sender来控制。wakeup只是一个通知,实际的工作还是由线程的run方法来控制的。同样调用client.send也只是把请求先放到队列中。
在客户端将消息发送给服务端之前,会调用RecordAccumulator.ready()方法获得集群中符合发送消息条件的节点集合。这些条件是站在RecordAccumulator角度对集群中的Node进行删选的,具体条件如下:
boolean sendable = full || expired || exhausted || closed || flushInProgress();
- Deque中有多个RecordBatch或是的第一个RecordBatch是否满了。
- 是否超时了。
- 是否有其他线程在等待BufferPool释放空间(即BufferPool的空间耗尽了)。
- Sender线程准备关闭。
- 是否有线程正在等待flush操作完成。
KafkaProducer(Map<String, Object> configs,
Serializer<K> keySerializer,
Serializer<V> valueSerializer,
ProducerMetadata metadata,
KafkaClient kafkaClient,
ProducerInterceptors interceptors,
Time time) {
...
// 创建Sender线程
this.sender = newSender(logContext, kafkaClient, this.metadata);
String ioThreadName = NETWORK_THREAD_PREFIX + " | " + clientId;
// 启动Sender对应的线程
this.ioThread = new KafkaThread(ioThreadName, this.sender, true);
this.ioThread.start();
...
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
private Future<RecordMetadata> doSend(ProducerRecord<K, V> record, Callback callback) {
...
if (result.batchIsFull || result.newBatchCreated) {
log.trace("Waking up the sender since topic {} partition {} is either full or getting a new batch", record.topic(), partition);
this.sender.wakeup();
}
}
KafkaProducer的构造方法中创建好了Sender线程,并将其放入了一个单独的ioThread,随后启动了这个ioThread线程。Sender实现了Runnable接口,并运行在单独的ioThread中。Sender的run()方法调用了重载的run()。run不需要用户手动调用。run()核心方法是调用runOnce()。
public class Sender implements Runnable {
public void run() {
// 一直运行,直到关闭,后台线程
// main loop, runs until close is called
while (running) {
try {
runOnce();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Uncaught error in kafka producer I/O thread: ", e);
}
}
// 不是强行停掉,则等待剩余请求处理完
// okay we stopped accepting requests but there may still be
// requests in the transaction manager, accumulator or waiting for acknowledgment,
// wait until these are completed.
while (!forceClose && ((this.accumulator.hasUndrained() || this.client.inFlightRequestCount() > 0) || hasPendingTransactionalRequests())) {
try {
runOnce();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Uncaught error in kafka producer I/O thread: ", e);
}
}
// Abort the transaction if any commit or abort didn't go through the transaction manager's queue
while (!forceClose && transactionManager != null && transactionManager.hasOngoingTransaction()) {
if (!transactionManager.isCompleting()) {
log.info("Aborting incomplete transaction due to shutdown");
transactionManager.beginAbort();
}
try {
runOnce();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Uncaught error in kafka producer I/O thread: ", e);
}
}
// 强行停止,忽略未完成的
if (forceClose) {
// We need to fail all the incomplete transactional requests and batches and wake up the threads waiting on
// the futures.
if (transactionManager != null) {
log.debug("Aborting incomplete transactional requests due to forced shutdown");
transactionManager.close();
}
log.debug("Aborting incomplete batches due to forced shutdown");
this.accumulator.abortIncompleteBatches();
}
try {
this.client.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Failed to close network client", e);
}
}
void runOnce() {
...
long currentTimeMs = time.milliseconds();
// 构造网络请求
long pollTimeout = sendProducerData(currentTimeMs);
// 网络I/O,将上面构造的请求通过网络发送到服务端
client.poll(pollTimeout, currentTimeMs);
}
}
Kafka的Sender线程核心发送方法就是sendProducerData,最后是调用了NetworkClient.poll()。
public class Sender implements Runnable {
private long sendProducerData(long now) {
// 1. 获取元数据集群信息
Cluster cluster = metadata.fetch();
// get the list of partitions with data ready to send
// 2. 获得集群中符合发送消息条件的节点集合
RecordAccumulator.ReadyCheckResult result = this.accumulator.ready(cluster, now);
if (!result.unknownLeaderTopics.isEmpty()) {
// 3. 存在未知leader的topics,加入metadata,标记需要更新标志位但是并没更新
// The set of topics with unknown leader contains topics with leader election pending as well as
// topics which may have expired. Add the topic again to metadata to ensure it is included
// and request metadata update, since there are messages to send to the topic.
for (String topic : result.unknownLeaderTopics)
this.metadata.add(topic);
log.debug("Requesting metadata update due to unknown leader topics from the batched records: {}",
result.unknownLeaderTopics);
this.metadata.requestUpdate();
}
// 4. 检查待发送的节点,移除不可用的节点
// remove any nodes we aren't ready to send to
Iterator<Node> iter = result.readyNodes.iterator();
long notReadyTimeout = Long.MAX_VALUE;
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Node node = iter.next();
// 调用client.ready()方法检查每个节点的网络I/O是否符合发送消息的条件,将不符合的节点移除
if (!this.client.ready(node, now)) {
iter.remove();
notReadyTimeout = Math.min(notReadyTimeout, this.client.pollDelayMs(node, now));
}
}
// create produce requests
// 5. 把发往相同leader的batch放一起,把<分区, 消息队列>的映射关系转换成<节点, 消息队列>的映射关系,tp.batch-->node.batch
Map<Integer, List<ProducerBatch>> batches = this.accumulator.drain(cluster, result.readyNodes, this.maxRequestSize, now);
// 使用addToInflightBatches方法将batches放入在途批次
addToInflightBatches(batches);
...
// 6. 将待发送的消息封装成ClientRequest请求
sendProduceRequests(batches, now);
return pollTimeout;
}
}
获得集群中符合发送消息条件的节点集合
public final class RecordAccumulator {
public ReadyCheckResult ready(Cluster cluster, long nowMs) {
// 储存可以发送的节点
Set<Node> readyNodes = new HashSet<>();
long nextReadyCheckDelayMs = Long.MAX_VALUE;
// 存储未知leader的topic
Set<String> unknownLeaderTopics = new HashSet<>();
// exhausted 标记了线程池的内存不足等待队列是否有东西,内存不足,赶紧发送
boolean exhausted = this.free.queued() > 0;
for (Map.Entry<TopicPartition, Deque<ProducerBatch>> entry : this.batches.entrySet()) {
Deque<ProducerBatch> deque = entry.getValue();
synchronized (deque) {
// When producing to a large number of partitions, this path is hot and deques are often empty.
// We check whether a batch exists first to avoid the more expensive checks whenever possible.
ProducerBatch batch = deque.peekFirst();
if (batch != null) {
TopicPartition part = entry.getKey();
// 遍历batches中的队列dq,从元数据找leader
Node leader = cluster.leaderFor(part);
// 如果没有找到对应主机。 unknownLeaderTopics
if (leader == null) {
// This is a partition for which leader is not known, but messages are available to send.
// Note that entries are currently not removed from batches when deque is empty.
unknownLeaderTopics.add(part.topic());
} else if (!readyNodes.contains(leader) && !isMuted(part, nowMs)) {
// batch.attempts:重试的次数
// batch.lastAttemptMs: 上一次重试的时间
// waitedTimeMs:当前时间 - 上一次重试的时间,已经等待了多久
// retryBackoffMs:重试的时间间隔
// backingOff:重新发送数据的时间到了
long waitedTimeMs = batch.waitedTimeMs(nowMs);
boolean backingOff = batch.attempts() > 0 && waitedTimeMs < retryBackoffMs;
// timeToWaitMs = linerMs = 100ms,最多能等待多久,消息最多存多久就必须要发送出去
long timeToWaitMs = backingOff ? retryBackoffMs : lingerMs;
// 如果队列大于1,说明这个队列里面至少有一个批次肯定是写满了。如果批次写满了肯定是可以发送数据。或者只有1个队列,刚好队列写满了,也可以发送
boolean full = deque.size() > 1 || batch.isFull();
boolean expired = waitedTimeMs >= timeToWaitMs;
// 判断可发送状态
// 1. full: 如果一个批次写满了(无论时间有没有到)
// 2. expired:时间到了(批次没写满也得发送)
// 3. exhausted:内存不够(消息发送出去以后,就会释放内存)
boolean sendable = full || expired || exhausted || closed || flushInProgress();
if (sendable && !backingOff) {
readyNodes.add(leader);
} else {
// 还要在等待多久
long timeLeftMs = Math.max(timeToWaitMs - waitedTimeMs, 0);
// Note that this results in a conservative estimate since an un-sendable partition may have
// a leader that will later be found to have sendable data. However, this is good enough
// since we'll just wake up and then sleep again for the remaining time.
nextReadyCheckDelayMs = Math.min(timeLeftMs, nextReadyCheckDelayMs);
}
}
}
}
}
return new ReadyCheckResult(readyNodes, nextReadyCheckDelayMs, unknownLeaderTopics);
}
}
ClientRequest 及创建请求

sendProduceRequests -> sendProduceRequest -> client.newClientRequest
private void sendProduceRequest(long now, int destination, short acks, int timeout, List<ProducerBatch> batches) {
//produceRecordsByPartition和recordsByPartition的value不一样,
Map<TopicPartition, MemoryRecords> produceRecordsByPartition = new HashMap<>(batches.size());
final Map<TopicPartition, ProducerBatch> recordsByPartition = new HashMap<>(batches.size());
for (ProducerBatch batch : batches) {
// 每个ProducerBatch都有唯一的TopicPartition
TopicPartition tp = batch.topicPartition;
// ProducerBatch的records是MemoryRecords,底层是ByteBuffer
MemoryRecords records = batch.records();
if (!records.hasMatchingMagic(minUsedMagic))
records = batch.records().downConvert(minUsedMagic, 0, time).records();
produceRecordsByPartition.put(tp, records);
recordsByPartition.put(tp, batch);
}
...
// 创建requestBuilder
ProduceRequest.Builder requestBuilder = ProduceRequest.Builder.forMagic(minUsedMagic, acks, timeout,
produceRecordsByPartition, transactionalId);
// 回调函数会作为客户端请求的一个成员变量, 当客户端请求完成后, 会触发回调函数的执行
RequestCompletionHandler callback = new RequestCompletionHandler() {
public void onComplete(ClientResponse response) {
// 设置结果回调方法,在handleProduceResponse对服务端返回结果进行处理
handleProduceResponse(response, recordsByPartition, time.milliseconds());
}
};
String nodeId = Integer.toString(destination);
// 每个nodeId生成一个clientRequest
ClientRequest clientRequest = client.newClientRequest(nodeId, requestBuilder, now, acks != 0,
requestTimeoutMs, callback);
// 将ClientRequest请求写进KafkaChannel的send属性,并且为KafkaChannel注册写入事件
client.send(clientRequest, now);
log.trace("Sent produce request to {}: {}", nodeId, requestBuilder);
}
将ClientRequest请求写进KafkaChannel的send属性,并且为KafkaChannel注册写入事件,调用client.send。
Network将请求放入KafkaChannel的缓存
client.send()调用NetwoekClient.send()将ClientRequest写入KafkaChannel的send字段。
Sender newSender(LogContext logContext, KafkaClient kafkaClient, ProducerMetadata metadata) {
ChannelBuilder channelBuilder = ClientUtils.createChannelBuilder(producerConfig, time);
KafkaClient client = kafkaClient != null ? kafkaClient : new NetworkClient(
new Selector(producerConfig.getLong(ProducerConfig.CONNECTIONS_MAX_IDLE_MS_CONFIG),
this.metrics, time, "producer", channelBuilder, logContext),
metadata,
clientId,
maxInflightRequests,
producerConfig.getLong(ProducerConfig.RECONNECT_BACKOFF_MS_CONFIG),
producerConfig.getLong(ProducerConfig.RECONNECT_BACKOFF_MAX_MS_CONFIG),
producerConfig.getInt(ProducerConfig.SEND_BUFFER_CONFIG),
producerConfig.getInt(ProducerConfig.RECEIVE_BUFFER_CONFIG),
requestTimeoutMs,
ClientDnsLookup.forConfig(producerConfig.getString(ProducerConfig.CLIENT_DNS_LOOKUP_CONFIG)),
time,
true,
apiVersions,
throttleTimeSensor,
logContext);
}
public class NetworkClient implements KafkaClient {
private void doSend(ClientRequest clientRequest, boolean isInternalRequest, long now, AbstractRequest request) {
// 要发送的目标brokerID
String destination = clientRequest.destination();
RequestHeader header = clientRequest.makeHeader(request.version());
...
// 将目标brokerID和请求头构成NetworkSend
Send send = request.toSend(destination, header);
InFlightRequest inFlightRequest = new InFlightRequest(
clientRequest,
header,
isInternalRequest,
request,
send,
now);
// inFlightRequests队列的作用是缓存已经发出去但没有收到响应的ClientRequest
this.inFlightRequests.add(inFlightRequest);
// 覆盖KafkaChannel的send字段,并为KafkaChannel注册写入事件
selector.send(send);
}
}
public class Selector implements Selectable, AutoCloseable {
public void send(Send send) {
String connectionId = send.destination();
KafkaChannel channel = openOrClosingChannelOrFail(connectionId);
if (closingChannels.containsKey(connectionId)) {
// ensure notification via `disconnected`, leave channel in the state in which closing was triggered
this.failedSends.add(connectionId);
} else {
try {
// 写入channel
channel.setSend(send);
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
}
}
}
// 给KafkaChannel.send 赋值,并写入注册事件
public class KafkaChannel implements AutoCloseable {
public void setSend(Send send) {
...
this.send = send;
this.transportLayer.addInterestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
}
Selector属于网络I/O层,它使用NIO异步非阻塞模式实现网络I/O操作。只有注册了写入事件,Selector才会把消息发送出去。
发送请求
client.poll调用NetworkClient.poll()方法,将KafkaChannel.send字段中保存的ClientRequest发送出去,并且处理服务端发回的响应、处理超时的请求、调用用户自定义的CallBack。
Do actual reads and writes to sockets.
public class NetworkClient implements KafkaClient {
public List<ClientResponse> poll(long timeout, long now) {
...
long metadataTimeout = metadataUpdater.maybeUpdate(now);
try {
this.selector.poll(Utils.min(timeout, metadataTimeout, defaultRequestTimeoutMs));
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("Unexpected error during I/O", e);
}
...
return responses;
}
}
public class Selector implements Selectable, AutoCloseable {
public void poll(long timeout) throws IOException {
if (timeout < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout should be >= 0");
boolean madeReadProgressLastCall = madeReadProgressLastPoll;
clear();
boolean dataInBuffers = !keysWithBufferedRead.isEmpty();
if (hasStagedReceives() || !immediatelyConnectedKeys.isEmpty() || (madeReadProgressLastCall && dataInBuffers))
timeout = 0;
if (!memoryPool.isOutOfMemory() && outOfMemory) {
//we have recovered from memory pressure. unmute any channel not explicitly muted for other reasons
log.trace("Broker no longer low on memory - unmuting incoming sockets");
for (KafkaChannel channel : channels.values()) {
if (channel.isInMutableState() && !explicitlyMutedChannels.contains(channel)) {
channel.maybeUnmute();
}
}
outOfMemory = false;
}
/* check ready keys */
long startSelect = time.nanoseconds();
int numReadyKeys = select(timeout);
long endSelect = time.nanoseconds();
this.sensors.selectTime.record(endSelect - startSelect, time.milliseconds());
if (numReadyKeys > 0 || !immediatelyConnectedKeys.isEmpty() || dataInBuffers) {
Set<SelectionKey> readyKeys = this.nioSelector.selectedKeys();
// Poll from channels that have buffered data (but nothing more from the underlying socket)
if (dataInBuffers) {
keysWithBufferedRead.removeAll(readyKeys); //so no channel gets polled twice
Set<SelectionKey> toPoll = keysWithBufferedRead;
keysWithBufferedRead = new HashSet<>(); //poll() calls will repopulate if needed
pollSelectionKeys(toPoll, false, endSelect);
}
// Poll from channels where the underlying socket has more data
pollSelectionKeys(readyKeys, false, endSelect);
// Clear all selected keys so that they are included in the ready count for the next select
readyKeys.clear();
pollSelectionKeys(immediatelyConnectedKeys, true, endSelect);
immediatelyConnectedKeys.clear();
} else {
madeReadProgressLastPoll = true; //no work is also "progress"
}
long endIo = time.nanoseconds();
this.sensors.ioTime.record(endIo - endSelect, time.milliseconds());
// Close channels that were delayed and are now ready to be closed
completeDelayedChannelClose(endIo);
// we use the time at the end of select to ensure that we don't close any connections that
// have just been processed in pollSelectionKeys
maybeCloseOldestConnection(endSelect);
// Add to completedReceives after closing expired connections to avoid removing
// channels with completed receives until all staged receives are completed.
addToCompletedReceives();
}
void pollSelectionKeys(Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys,
boolean isImmediatelyConnected,
long currentTimeNanos) {
for (SelectionKey key : determineHandlingOrder(selectionKeys)) {
KafkaChannel channel = channel(key);
long channelStartTimeNanos = recordTimePerConnection ? time.nanoseconds() : 0;
boolean sendFailed = false;
...
try {
// 如果connect返回true或OP_CONNECT,监听到连接事件
/* complete any connections that have finished their handshake (either normally or immediately) */
if (isImmediatelyConnected || key.isConnectable()) {
// finishConnect()先检测socketChannel是否建立成功,然后会注册读事件
if (channel.finishConnect()) {
// channel放入conneted
this.connected.add(channel.id());
this.sensors.connectionCreated.record();
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
log.debug("Created socket with SO_RCVBUF = {}, SO_SNDBUF = {}, SO_TIMEOUT = {} to node {}",
socketChannel.socket().getReceiveBufferSize(),
socketChannel.socket().getSendBufferSize(),
socketChannel.socket().getSoTimeout(),
channel.id());
} else {
continue;
}
}
...
// 处理读事件
attemptRead(key, channel);
// 如果还有数据未读取完,把selectionKeys缓存在keysWithBufferedRead中
if (channel.hasBytesBuffered()) {
keysWithBufferedRead.add(key);
}
// 处理写事件
if (channel.ready() && key.isWritable() && !channel.maybeBeginClientReauthentication(
() -> channelStartTimeNanos != 0 ? channelStartTimeNanos : currentTimeNanos)) {
Send send;
try {
// 将buffer中的消息数据写入到通道中,返回ByteBufferSend
send = channel.write();
} catch (Exception e) {
sendFailed = true;
throw e;
}
if (send != null) {
// 记录已经完成的send
this.completedSends.add(send);
this.sensors.recordBytesSent(channel.id(), send.size());
}
}
/* cancel any defunct sockets */
if (!key.isValid())
// 关闭连接
close(channel, CloseMode.GRACEFUL);
} catch (Exception e) {
...
} finally {
maybeRecordTimePerConnection(channel, channelStartTimeNanos);
}
}
}
}
pollSelectionKeys(readyKeys, false, endSelect) 执行网络I/O操作的核心,它需要传入一个SelectionKey集合,用于后面获取KafkaChannel。KafkaChannel注册了写入事件,所以这里能够通过SelectionKey获取到KafkaChannel对象。
- OP_CONNECT:处理一些刚建立 tcp 连接的 channel
- OP_WRITE:channel 发送消息
- OP_READ:channel读取返回的数据
tcp粘包拆包
通常有哪些解决粘包拆包问题的方法?
- 定长
- 分隔符
- 自定义协议,如len + data
kafka使用长度编码,在报文的最开始数个字节(常见为4个字节,足以编码4个G长度,相比之下两个字节仅能存放64K消息),声明报文剩余内容的长度。
public class Selector implements Selectable, AutoCloseable {
private void attemptRead(SelectionKey key, KafkaChannel channel) throws IOException {
//if channel is ready and has bytes to read from socket or buffer, and has no
//previous receive(s) already staged or otherwise in progress then read from it
if (channel.ready() && (key.isReadable() || channel.hasBytesBuffered()) && !hasStagedReceive(channel)
&& !explicitlyMutedChannels.contains(channel)) {
NetworkReceive networkReceive;
// 一次性收到很多条数据的时候,会如何处理呢?
// 一次性读取所有的receives,暂存到stageReceives中
while ((networkReceive = channel.read()) != null) {
madeReadProgressLastPoll = true;
addToStagedReceives(channel, networkReceive);
}
// isMute是判断当前channel是否关注了OP_READ事件
if (channel.isMute()) {
outOfMemory = true; //channel has muted itself due to memory pressure.
} else {
madeReadProgressLastPoll = true;
}
}
}
}
channel.read()
public class KafkaChannel implements AutoCloseable {
public NetworkReceive read() throws IOException {
NetworkReceive result = null;
// 新建一个receive
if (receive == null) {
receive = new NetworkReceive(maxReceiveSize, id, memoryPool);
}
// 真正的数据read
receive(receive);
// 数据读取完成的后置操作
// receive.complete()是对接受的消息进行判断是否完整
if (receive.complete()) {
// 倒带,等待读
receive.payload().rewind();
// 直接引用赋值
result = receive;
// 最后清空当前引用,然后等待下次进入read的时候,执行new 操作
receive = null;
} else if (receive.requiredMemoryAmountKnown() && !receive.memoryAllocated() && isInMutableState()) {
//pool must be out of memory, mute ourselves.
mute();
}
return result;
}
private long receive(NetworkReceive receive) throws IOException {
return receive.readFrom(transportLayer);
}
}
public class NetworkReceive implements Receive {
public NetworkReceive(int maxSize, String source, MemoryPool memoryPool) {
this.source = source;
// 4个字节
this.size = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
this.buffer = null;
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.memoryPool = memoryPool;
}
public long readFrom(ScatteringByteChannel channel) throws IOException {
// 存在数据
int read = 0;
// len + data
if (size.hasRemaining()) {
int bytesRead = channel.read(size);
if (bytesRead < 0)
throw new EOFException();
read += bytesRead;
// 如果读满了长度,则直接倒带得到具体的len值
// 这里的size是一个byteBuffer类型的,也就是接收到的数据
if (!size.hasRemaining()) {
size.rewind();
// 先读取前4字节,转换为一个int,即长度
int receiveSize = size.getInt();
if (receiveSize < 0)
throw new InvalidReceiveException("Invalid receive (size = " + receiveSize + ")");
if (maxSize != UNLIMITED && receiveSize > maxSize)
throw new InvalidReceiveException("Invalid receive (size = " + receiveSize + " larger than " + maxSize + ")");
requestedBufferSize = receiveSize; //may be 0 for some payloads (SASL)
if (receiveSize == 0) {
buffer = EMPTY_BUFFER;
}
}
}
// 根据接收长度申请数据data需要的buffer
if (buffer == null && requestedBufferSize != -1) { //we know the size we want but havent been able to allocate it yet
buffer = memoryPool.tryAllocate(requestedBufferSize);
if (buffer == null)
log.trace("Broker low on memory - could not allocate buffer of size {} for source {}", requestedBufferSize, source);
}
// 申请完毕之后,就调用read函数,直接read出来即可
if (buffer != null) {
int bytesRead = channel.read(buffer);
if (bytesRead < 0)
throw new EOFException();
read += bytesRead;
}
// 返回读取的总字节数
return read;
}
}
用addToStagedReceives(channel, networkReceive)把返回的receive放进stagedReceives中,一个channel对应一个队列存放这些返回的receive。
receive方法解决了粘包拆包问题,size是一个固定大小的bytebuffer用来装receive消息体的大小。分配size大小的bytebuffer后读数据,去channel读数据进buffer。
拆包,也就是接收到数据不够组成一条完整的数据,该如何等待完整的数据包?
receive.complete()函数的判断逻辑,只要一条数据没读完整,那么receive.complete()函数返回值就是false,那么最终返回的结果就是null,等待下一次OP_READ事件的时候再接着上次没读完的数据读取,直到读取一条完整的数据为止。
- !size.hasRemaining():接收到的buffer数据已经读取完成
- buffer != null:buffer已经创建
- !buffer.hasRemaining():buffer已经读取完成
public boolean complete() {
return !size.hasRemaining() && buffer != null && !buffer.hasRemaining();
}
selector.poll()的pollSelectionKeys之后,addToCompletedReceives方法对 stagedReceives进行处理,stagedReceives不空的情况下,取出channel对应的存放NetworkReceive的dq存入。完成响应的存储。
private void addToCompletedReceives() {
if (!this.stagedReceives.isEmpty()) {
Iterator<Map.Entry<KafkaChannel, Deque<NetworkReceive>>> iter = this.stagedReceives.entrySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<KafkaChannel, Deque<NetworkReceive>> entry = iter.next();
KafkaChannel channel = entry.getKey();
if (!explicitlyMutedChannels.contains(channel)) {
Deque<NetworkReceive> deque = entry.getValue();
addToCompletedReceives(channel, deque);
if (deque.isEmpty())
iter.remove();
}
}
}
}
private void addToCompletedReceives(KafkaChannel channel, Deque<NetworkReceive> stagedDeque) {
NetworkReceive networkReceive = stagedDeque.poll();
this.completedReceives.add(networkReceive);
this.sensors.recordBytesReceived(channel.id(), networkReceive.size());
}
生产者处理响应数据

public class NetworkClient implements KafkaClient {
public List<ClientResponse> poll(long timeout, long now) {
...
long metadataTimeout = metadataUpdater.maybeUpdate(now);
try {
this.selector.poll(Utils.min(timeout, metadataTimeout, defaultRequestTimeoutMs));
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("Unexpected error during I/O", e);
}
long updatedNow = this.time.milliseconds();
List<ClientResponse> responses = new ArrayList<>();
// 对发送出去的send 不需要响应的做了处理。
handleCompletedSends(responses, updatedNow);
// 对pollSelectionKeys中获取的响应进行处理
handleCompletedReceives(responses, updatedNow);
handleDisconnections(responses, updatedNow);
handleConnections();
handleInitiateApiVersionRequests(updatedNow);
handleTimedOutRequests(responses, updatedNow);
// 回调函数是在kafka producer 的run方法传入,一路传入,在networkClient的completeResponse阶段触发
completeResponses(responses);
return responses;
}
private void handleCompletedReceives(List<ClientResponse> responses, long now) {
for (NetworkReceive receive : this.selector.completedReceives()) {
String source = receive.source();
InFlightRequest req = inFlightRequests.completeNext(source);
Struct responseStruct = parseStructMaybeUpdateThrottleTimeMetrics(receive.payload(), req.header,
throttleTimeSensor, now);
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Completed receive from node {} for {} with correlation id {}, received {}", req.destination,
req.header.apiKey(), req.header.correlationId(), responseStruct);
}
// If the received response includes a throttle delay, throttle the connection.
AbstractResponse body = AbstractResponse.
parseResponse(req.header.apiKey(), responseStruct, req.header.apiVersion());
maybeThrottle(body, req.header.apiVersion(), req.destination, now);
// 返回的是元数据请求,去更新元数据
if (req.isInternalRequest && body instanceof MetadataResponse)
metadataUpdater.handleSuccessfulResponse(req.header, now, (MetadataResponse) body);
// 版本协调信息
else if (req.isInternalRequest && body instanceof ApiVersionsResponse)
handleApiVersionsResponse(responses, req, now, (ApiVersionsResponse) body);
else
// 正常返回消息
responses.add(req.completed(body, now));
}
}
}
response.onComplete(),调用callback
public void onComplete() {
if (callback != null)
callback.onComplete(this);
}
其他
参考资料
- 《kafka技术内幕》
- kafka官网 https://kafka.apache.org/documentation.html
- kafka源码 https://blog.csdn.net/bohu83/article/details/88563955
- kafka元数据初始化和拉取全流程 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/410804288
- kafka源码解析生产者解析之内存池 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/411807763
- kafka内存池 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/430328244
- kafka专题 https://my.oschina.net/keepal?tab=newest&catalogId=7217403