Kafka源码02(Broker)
BrokerStates
Broker 状态
/**
* Broker states are the possible state that a kafka broker can be in.
* A broker should be only in one state at a time.
* The expected state transition with the following defined states is:
*
* +-----------+
* |Not Running|
* +-----+-----+
* |
* v
* +-----+-----+
* |Starting +--+
* +-----+-----+ | +----+------------+
* | +>+RecoveringFrom |
* v |UncleanShutdown |
* +-------+-------+ +-------+---------+
* |RunningAsBroker| |
* +-------+-------+<-----------+
* |
* v
* +-----+------------+
* |PendingControlled |
* |Shutdown |
* +-----+------------+
* |
* v
* +-----+----------+
* |BrokerShutting |
* |Down |
* +-----+----------+
* |
* v
* +-----+-----+
* |Not Running|
* +-----------+
*
* Custom states is also allowed for cases where there are custom kafka states for different scenarios.
*/
sealed trait BrokerStates { def state: Byte }
case object NotRunning extends BrokerStates { val state: Byte = 0 }
case object Starting extends BrokerStates { val state: Byte = 1 }
case object RecoveringFromUncleanShutdown extends BrokerStates { val state: Byte = 2 }
case object RunningAsBroker extends BrokerStates { val state: Byte = 3 }
case object PendingControlledShutdown extends BrokerStates { val state: Byte = 6 }
case object BrokerShuttingDown extends BrokerStates { val state: Byte = 7 }
KafkaConfig
Kafka服务器的配置设置,可通过加载一个Properties文件加载配置,封装了配置和默认值
num.network.threads=3
num.io.threads=8
KafkaServerStartable
根据配置信息调用KafkaServer创建一个kafka服务器,并提供了startup和shutdown方法分别用于启动和关闭Kafka服务器。另外还提供了一个setServerState可以设置该Broker的状态。
KafkaServer
管理一个Kafka broker的生命周期。处理所有的功能,包括启动和关闭一个Kafka节点。
class KafkaServer() {
// 开启一个Kafka server,初始化LogManager, SocketServer和请求处理器
def startup(): Unit = {
try {
info("starting")
if (isShuttingDown.get)
throw new IllegalStateException("Kafka server is still shutting down, cannot re-start!")
if (startupComplete.get)
return
val canStartup = isStartingUp.compareAndSet(false, true)
if (canStartup) {
// 1. 设置broker状态为STARTING状态
brokerState.newState(Starting)
// 2. 设置zookeeper
/* setup zookeeper */
initZkClient(time)
// 3. 获取集群id
/* Get or create cluster_id */
_clusterId = getOrGenerateClusterId(zkClient)
info(s"Cluster ID = $clusterId")
/* load metadata */
val (preloadedBrokerMetadataCheckpoint, initialOfflineDirs) = getBrokerMetadataAndOfflineDirs
/* check cluster id */
if (preloadedBrokerMetadataCheckpoint.clusterId.isDefined && preloadedBrokerMetadataCheckpoint.clusterId.get != clusterId)
throw new InconsistentClusterIdException(
s"The Cluster ID ${clusterId} doesn't match stored clusterId ${preloadedBrokerMetadataCheckpoint.clusterId} in meta.properties. " +
s"The broker is trying to join the wrong cluster. Configured zookeeper.connect may be wrong.")
/* generate brokerId */
config.brokerId = getOrGenerateBrokerId(preloadedBrokerMetadataCheckpoint)
logContext = new LogContext(s"[KafkaServer id=${config.brokerId}] ")
this.logIdent = logContext.logPrefix
// initialize dynamic broker configs from ZooKeeper. Any updates made after this will be
// applied after DynamicConfigManager starts.
// 向zookeeper注册broker动态配置属性
config.dynamicConfig.initialize(zkClient)
// 4. 启动调度器
/* start scheduler */
kafkaScheduler = new KafkaScheduler(config.backgroundThreads)
kafkaScheduler.startup()
/* create and configure metrics */
val reporters = new util.ArrayList[MetricsReporter]
reporters.add(new JmxReporter(jmxPrefix))
val metricConfig = KafkaServer.metricConfig(config)
metrics = new Metrics(metricConfig, reporters, time, true)
/* register broker metrics */
_brokerTopicStats = new BrokerTopicStats
quotaManagers = QuotaFactory.instantiate(config, metrics, time, threadNamePrefix.getOrElse(""))
notifyClusterListeners(kafkaMetricsReporters ++ metrics.reporters.asScala)
logDirFailureChannel = new LogDirFailureChannel(config.logDirs.size)
// 5. 启动日志管理器
/* start log manager */
logManager = LogManager(config, initialOfflineDirs, zkClient, brokerState, kafkaScheduler, time, brokerTopicStats, logDirFailureChannel)
logManager.startup()
// 6. 元数据缓存
metadataCache = new MetadataCache(config.brokerId)
// Enable delegation token cache for all SCRAM mechanisms to simplify dynamic update.
// This keeps the cache up-to-date if new SCRAM mechanisms are enabled dynamically.
tokenCache = new DelegationTokenCache(ScramMechanism.mechanismNames)
credentialProvider = new CredentialProvider(ScramMechanism.mechanismNames, tokenCache)
// Create and start the socket server acceptor threads so that the bound port is known.
// Delay starting processors until the end of the initialization sequence to ensure
// that credentials have been loaded before processing authentications.
// 7. 创建broker上的SocketServer并启动,NIO的服务端
socketServer = new SocketServer(config, metrics, time, credentialProvider)
socketServer.startup(startupProcessors = false)
// 8. 创建副本管理器并启动
/* start replica manager */
replicaManager = createReplicaManager(isShuttingDown)
replicaManager.startup()
val brokerInfo = createBrokerInfo
val brokerEpoch = zkClient.registerBroker(brokerInfo)
// Now that the broker is successfully registered, checkpoint its metadata
checkpointBrokerMetadata(BrokerMetadata(config.brokerId, Some(clusterId)))
/* start token manager */
tokenManager = new DelegationTokenManager(config, tokenCache, time , zkClient)
tokenManager.startup()
// 9. 开启KafkaController
/* start kafka controller */
// broker 0,broker 1,broker 2,启动完了从里面选举出来一个controller节点,作为主节点,用来管理整个Kafka集群
kafkaController = new KafkaController(config, zkClient, time, metrics, brokerInfo, brokerEpoch, tokenManager, threadNamePrefix)
kafkaController.startup()
adminManager = new AdminManager(config, metrics, metadataCache, zkClient)
// 10. 启动 group coordinator
// group coordinator是负责进行 consumer 的 group 成员与 offset 管理
/* start group coordinator */
// Hardcode Time.SYSTEM for now as some Streams tests fail otherwise, it would be good to fix the underlying issue
groupCoordinator = GroupCoordinator(config, zkClient, replicaManager, Time.SYSTEM, metrics)
groupCoordinator.startup()
// 协调事务的,https://blog.csdn.net/cq_pf/article/details/106266505
/* start transaction coordinator, with a separate background thread scheduler for transaction expiration and log loading */
// Hardcode Time.SYSTEM for now as some Streams tests fail otherwise, it would be good to fix the underlying issue
transactionCoordinator = TransactionCoordinator(config, replicaManager, new KafkaScheduler(threads = 1, threadNamePrefix = "transaction-log-manager-"), zkClient, metrics, metadataCache, Time.SYSTEM)
transactionCoordinator.startup()
/* Get the authorizer and initialize it if one is specified.*/
authorizer = config.authorizer
authorizer.foreach(_.configure(config.originals))
val authorizerFutures: Map[Endpoint, CompletableFuture[Void]] = authorizer match {
case Some(authZ) =>
authZ.start(brokerInfo.broker.toServerInfo(clusterId, config)).asScala.mapValues(_.toCompletableFuture).toMap
case None =>
brokerInfo.broker.endPoints.map { ep => ep.toJava -> CompletableFuture.completedFuture[Void](null) }.toMap
}
val fetchManager = new FetchManager(Time.SYSTEM,
new FetchSessionCache(config.maxIncrementalFetchSessionCacheSlots,
KafkaServer.MIN_INCREMENTAL_FETCH_SESSION_EVICTION_MS))
/* start processing requests */
dataPlaneRequestProcessor = new KafkaApis(socketServer.dataPlaneRequestChannel, replicaManager, adminManager, groupCoordinator, transactionCoordinator,
kafkaController, zkClient, config.brokerId, config, metadataCache, metrics, authorizer, quotaManagers,
fetchManager, brokerTopicStats, clusterId, time, tokenManager)
// 11. 处理队列里面的请求的 numIoThreads 默认 8
dataPlaneRequestHandlerPool = new KafkaRequestHandlerPool(config.brokerId, socketServer.dataPlaneRequestChannel, dataPlaneRequestProcessor, time,
config.numIoThreads, s"${SocketServer.DataPlaneMetricPrefix}RequestHandlerAvgIdlePercent", SocketServer.DataPlaneThreadPrefix)
socketServer.controlPlaneRequestChannelOpt.foreach { controlPlaneRequestChannel =>
controlPlaneRequestProcessor = new KafkaApis(controlPlaneRequestChannel, replicaManager, adminManager, groupCoordinator, transactionCoordinator,
kafkaController, zkClient, config.brokerId, config, metadataCache, metrics, authorizer, quotaManagers,
fetchManager, brokerTopicStats, clusterId, time, tokenManager)
controlPlaneRequestHandlerPool = new KafkaRequestHandlerPool(config.brokerId, socketServer.controlPlaneRequestChannelOpt.get, controlPlaneRequestProcessor, time,
1, s"${SocketServer.ControlPlaneMetricPrefix}RequestHandlerAvgIdlePercent", SocketServer.ControlPlaneThreadPrefix)
}
Mx4jLoader.maybeLoad()
/* Add all reconfigurables for config change notification before starting config handlers */
config.dynamicConfig.addReconfigurables(this)
// 12. 创建topic配置管理器并启动
/* start dynamic config manager */
dynamicConfigHandlers = Map[String, ConfigHandler](ConfigType.Topic -> new TopicConfigHandler(logManager, config, quotaManagers, kafkaController),
ConfigType.Client -> new ClientIdConfigHandler(quotaManagers),
ConfigType.User -> new UserConfigHandler(quotaManagers, credentialProvider),
ConfigType.Broker -> new BrokerConfigHandler(config, quotaManagers))
// Create the config manager. start listening to notifications
dynamicConfigManager = new DynamicConfigManager(zkClient, dynamicConfigHandlers)
dynamicConfigManager.startup()
// 13. 启动 socketServer 的 Processor
socketServer.startControlPlaneProcessor(authorizerFutures)
socketServer.startDataPlaneProcessors(authorizerFutures)
// 14. 设置broker状态为RUNNINGASBROKER
brokerState.newState(RunningAsBroker)
shutdownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1)
// 15. 新的broker已经启动
startupComplete.set(true)
isStartingUp.set(false)
AppInfoParser.registerAppInfo(jmxPrefix, config.brokerId.toString, metrics, time.milliseconds())
info("started")
}
}
catch {
case e: Throwable =>
fatal("Fatal error during KafkaServer startup. Prepare to shutdown", e)
isStartingUp.set(false)
shutdown()
throw e
}
}
}
initZkClient 设置zookeeper
initZkClient -> createZkClient -> KafkaZkClient -> ZooKeeperClient
KafkaZkClient 类主要提供kafka操作zookeeper。
ZooKeeperClient 封装了pipelined requests和zk操作。信号量用来控制同时访问特定资源的线程数量,通过协调各个线程,以保证合理的使用资源。响应存储到响应队列。
最大执行中请求数
val ZkMaxInFlightRequests = 10
private def initZkClient(time: Time): Unit = {
// 创建client
_zkClient = createZkClient(config.zkConnect, secureAclsEnabled)
// 初始化路径信息
_zkClient.createTopLevelPaths()
}
val PersistentZkPaths = Seq(
ConsumerPathZNode.path, // old consumer path /consumers
BrokerIdsZNode.path, // /brokers/ids
TopicsZNode.path, // /brokers/topics
ConfigEntityChangeNotificationZNode.path, // /config/changes
DeleteTopicsZNode.path, // admin/delete_topics
BrokerSequenceIdZNode.path, // /brokers/seqid
IsrChangeNotificationZNode.path, // /isr_change_notification
ProducerIdBlockZNode.path, // /latest_producer_id_block
LogDirEventNotificationZNode.path // log_dir_event_notification
) ++ ConfigType.all.map(ConfigEntityTypeZNode.path)
KafkaScheduler
A scheduler based on java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
val BackgroundThreads = 10
KafkaScheduler作为broker进程的调度模块,提供对线程池的封装,对于一些周期性/非周期性执行的逻辑,可用于周期性调度/非周期调度。
| 模块 | 定时任务 | 参数 | 默认 | 执行逻辑 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LogManager | cleanupLogs | log.retention.check.interval.ms | 300s | 过期日志文件清理 | |
| LogManager | flushDirtyLogs | log.flush.scheduler.interval.ms | Integer.Max | 刷日志到日盘 | |
| LogManager | checkpointLogRecoveryOffsets | log.flush.offset.checkpoint.interval.ms | 60s | 将topicandpartition的checkpoint写入磁盘 | 写入文件recovery-point-offset-checkpoint |
| LogManager | checkpointLogStartOffsets | log.flush.start.offset.checkpoint.interval.ms | 60s | 将offset的checkpoint写入磁盘 | |
| ReplicaManager | checkpointHighWatermarks | replica.high.watermark.checkpoint.interval.ms | 5s | 对hw进行checkpoint 写入文件 | replication-offset-checkpoint |
| ReplicaManager | maybeShrinkIsr | replica.lag.time.max.ms | 10s | 检查是否需要减少isr列表中的replica | |
| ReplicaManager | maybePropagateIsrChanges | NA | 2.5s | 检查是否生成/广播ISr列表/需要写入zk | zk目录为/isr_change_notification/isr_change_ |
| GroupMetadataManager | deleteExpiredOffsets | offsets.retention.check.interval.ms | 600s | 删除过期的offset 一天之后失效 | |
| ZookeeperConsumerConnector | autoCommit | auto.commit.interval.ms | 60s | 打开自动commit的场景下有效,默认值AutoCommitInterval,默认存储在zk,可以设置存储在kafka,以及zk | |
| KafkaController | checkAndTriggerPartitionRebalance | leader.imbalance.check.interval.seconds | 300s | 执行分区均衡 | 打开自动分区均衡的场景下有效,当分区leader不在perferred节点比例大于leader.imbalance.per.broker.percentage/100时(默认10%),进行 |
非周期调度
| 模块 | 定时任务 | 参数 | 默认 | 执行逻辑 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LogManager | deleteLogs | NA | NA | 该任务执行的任务主要是删除分区目录,同时删除底下的segment数据文件。 | |
| Log | flush(newOffset) | NA | NA | flush日志到磁盘 | roll方法中调用 |
| Log | deleteSeg | NA | NA | 删除segment 删除前会先修改log和index文件后缀.deleted | |
| GroupMetadataManager | loadGroupsAndOffsets | NA | NA | 加载partition的group和offset信息 | 在_offset_consumer的partition变为leader时执行 |
| GroupMetadataManager | removeGroupsAndOffsets | NA | NA | 去除partition的group和offset信息 | 在_offset_consumer的partition变为follower时执行 |
Log
/**
* An append-only log for storing messages.
* The log is a sequence of LogSegments, each with a base offset denoting the first message in the segment.
*/
class Log() {
// LogSegment 集合,SkipList 结构,以 baseOffset 作为 key,以 LogSegment 对象作为 value
private val segments: ConcurrentNavigableMap[java.lang.Long, LogSegment] = new ConcurrentSkipListMap[java.lang.Long, LogSegment]
}
- segments是线程安全的,这样 Kafka 源码不需要自行确保日志段操作过程中的线程安全
- segments是键值(Key)可排序的 Map。Kafka 将每个日志段的起始位移值作为 Key,能够很方便地根据所有日志段的起始位移值对它们进行排序和比较,同时还能快速地找到与给定位移值相近的前后两个日志段。
LogManager
LogManager是kafka的子系统,负责log的创建,检索及清理。所有的读写操作由单个的日志实例来代理。
初始化过程,loadLogs()
loadLogs执行加载每个 log 目录下的日志文件,并为每个 topic 分区对应的日志目录创建一个 Log 对象,对于标记为需要删除的 topic 分区目录(对应-delete后缀的目录),则将其 Log 对象添加到 LogManager.logsToBeDeleted 字段中,等待后面的周期性任务(kafka-delete-logs)对其进行删除。
Start the background threads to flush logs and do log cleanup
class LogManager() {
loadLogs()
/**
* Recover and load all logs in the given data directories
*/
private def loadLogs(): Unit = {
info("Loading logs.")
val startMs = time.milliseconds
val threadPools = ArrayBuffer.empty[ExecutorService]
val offlineDirs = mutable.Set.empty[(String, IOException)]
val jobs = mutable.Map.empty[File, Seq[Future[_]]]
// 遍历处理每个 log 目录
for (dir <- liveLogDirs) {
try {
// 为每个 log 目录创建一个 ioThreads 大小的线程池
val pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(numRecoveryThreadsPerDataDir)
threadPools.append(pool)
// 尝试获取 .kafka_cleanshutdown 文件,如果该文件存在则说明 broker 节点是正常关闭的
val cleanShutdownFile = new File(dir, Log.CleanShutdownFile)
if (cleanShutdownFile.exists) {
debug(s"Found clean shutdown file. Skipping recovery for all logs in data directory: ${dir.getAbsolutePath}")
} else {
// log recovery itself is being performed by `Log` class during initialization
// 当前 broker 不是正常关闭,设置 broker 状态为 RecoveringFromUncleanShutdown,表示正在从上次异常关闭中恢复
brokerState.newState(RecoveringFromUncleanShutdown)
}
// 读取每个 log 目录下的 recovery-point-offset-checkpoint 文件,返回 topic 分区对象与 HW 之间的映射关系
var recoveryPoints = Map[TopicPartition, Long]()
try {
recoveryPoints = this.recoveryPointCheckpoints(dir).read
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
warn(s"Error occurred while reading recovery-point-offset-checkpoint file of directory $dir", e)
warn("Resetting the recovery checkpoint to 0")
}
var logStartOffsets = Map[TopicPartition, Long]()
try {
logStartOffsets = this.logStartOffsetCheckpoints(dir).read
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
warn(s"Error occurred while reading log-start-offset-checkpoint file of directory $dir", e)
}
// 遍历当前 log 目录的子目录,仅处理目录,忽略文件
val jobsForDir = for {
dirContent <- Option(dir.listFiles).toList
logDir <- dirContent if logDir.isDirectory
} yield {
// 为每个 Log 目录创建一个 Runnable 任务
CoreUtils.runnable {
try {
// 调用loadLog 创建log对象
loadLog(logDir, recoveryPoints, logStartOffsets)
} catch {
case e: IOException =>
offlineDirs.add((dir.getAbsolutePath, e))
error(s"Error while loading log dir ${dir.getAbsolutePath}", e)
}
}
}
// 提交上面创建的任务,并将提交结果封装到 jobs 集合中,jobsForDir 是 List[Runnable] 类型
jobs(cleanShutdownFile) = jobsForDir.map(pool.submit)
} catch {
case e: IOException =>
offlineDirs.add((dir.getAbsolutePath, e))
error(s"Error while loading log dir ${dir.getAbsolutePath}", e)
}
}
// 阻塞等待上面提交的任务执行完成,即等待所有 log 目录下 topic 分区对应的目录文件加载完成
try {
for ((cleanShutdownFile, dirJobs) <- jobs) {
dirJobs.foreach(_.get)
try {
// 删除对应的 .kafka_cleanshutdown 文件
cleanShutdownFile.delete()
} catch {
case e: IOException =>
offlineDirs.add((cleanShutdownFile.getParent, e))
error(s"Error while deleting the clean shutdown file $cleanShutdownFile", e)
}
}
offlineDirs.foreach { case (dir, e) =>
logDirFailureChannel.maybeAddOfflineLogDir(dir, s"Error while deleting the clean shutdown file in dir $dir", e)
}
} catch {
case e: ExecutionException =>
error(s"There was an error in one of the threads during logs loading: ${e.getCause}")
throw e.getCause
} finally {
// 遍历关闭线程池
threadPools.foreach(_.shutdown())
}
info(s"Logs loading complete in ${time.milliseconds - startMs} ms.")
}
private def loadLog(logDir: File, recoveryPoints: Map[TopicPartition, Long], logStartOffsets: Map[TopicPartition, Long]): Unit = {
debug(s"Loading log '${logDir.getName}'")
// 依据目录名解析得到对应的 topic 分区对象
val topicPartition = Log.parseTopicPartitionName(logDir)
// 获取当前 topic 分区对应的配置
val config = topicConfigs.getOrElse(topicPartition.topic, currentDefaultConfig)
// 获取 topic 分区对应的 HW 值
val logRecoveryPoint = recoveryPoints.getOrElse(topicPartition, 0L)
val logStartOffset = logStartOffsets.getOrElse(topicPartition, 0L)
// 创建对应的 Log 对象,每个 topic 分区目录对应一个 Log 对象
val log = Log(
dir = logDir,
config = config,
logStartOffset = logStartOffset,
recoveryPoint = logRecoveryPoint,
maxProducerIdExpirationMs = maxPidExpirationMs,
producerIdExpirationCheckIntervalMs = LogManager.ProducerIdExpirationCheckIntervalMs,
scheduler = scheduler,
time = time,
brokerTopicStats = brokerTopicStats,
logDirFailureChannel = logDirFailureChannel)
// 如果当前 log 是需要被删除的文件,topic被删除,则记录到 logsToBeDeleted 队列中,会有周期性任务对其执行删除操作
if (logDir.getName.endsWith(Log.DeleteDirSuffix)) {
addLogToBeDeleted(log)
} else {
// 建立 topic 分区对象与其 Log 对象之间的映射关系,不允许一个 topic 分区对象对应多个目录
val previous = {
if (log.isFuture)
this.futureLogs.put(topicPartition, log)
else
this.currentLogs.put(topicPartition, log)
}
if (previous != null) {
if (log.isFuture)
throw new IllegalStateException("Duplicate log directories found: %s, %s!".format(log.dir.getAbsolutePath, previous.dir.getAbsolutePath))
else
throw new IllegalStateException(s"Duplicate log directories for $topicPartition are found in both ${log.dir.getAbsolutePath} " +
s"and ${previous.dir.getAbsolutePath}. It is likely because log directory failure happened while broker was " +
s"replacing current replica with future replica. Recover broker from this failure by manually deleting one of the two directories " +
s"for this partition. It is recommended to delete the partition in the log directory that is known to have failed recently.")
}
}
}
/**
* Start the background threads to flush logs and do log cleanup
*/
def startup(): Unit = {
/* Schedule the cleanup task to delete old logs */
if (scheduler != null) {
info("Starting log cleanup with a period of %d ms.".format(retentionCheckMs))
scheduler.schedule("kafka-log-retention",
cleanupLogs _,
delay = InitialTaskDelayMs,
period = retentionCheckMs,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
info("Starting log flusher with a default period of %d ms.".format(flushCheckMs))
scheduler.schedule("kafka-log-flusher",
flushDirtyLogs _,
delay = InitialTaskDelayMs,
period = flushCheckMs,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
scheduler.schedule("kafka-recovery-point-checkpoint",
checkpointLogRecoveryOffsets _,
delay = InitialTaskDelayMs,
period = flushRecoveryOffsetCheckpointMs,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
scheduler.schedule("kafka-log-start-offset-checkpoint",
checkpointLogStartOffsets _,
delay = InitialTaskDelayMs,
period = flushStartOffsetCheckpointMs,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
scheduler.schedule("kafka-delete-logs", // will be rescheduled after each delete logs with a dynamic period
deleteLogs _,
delay = InitialTaskDelayMs,
unit = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
}
if (cleanerConfig.enableCleaner)
cleaner.startup()
}
}
旧的日志段删除任务
在LogManager启动后,会提交一个周期性的日志段删除任务,用来处理一些超过一定时间以及大小的日志段。这个任务的执行周期和log.retention.check.interval.ms有关系,默认值是300000,也就是每5分钟执行一次删除任务。
class LogManager() {
/**
* Delete any eligible logs. Return the number of segments deleted.
* Only consider logs that are not compacted.
*/
def cleanupLogs(): Unit = {
debug("Beginning log cleanup...")
var total = 0
val startMs = time.milliseconds
// clean current logs.
val deletableLogs = {
if (cleaner != null) {
// prevent cleaner from working on same partitions when changing cleanup policy
cleaner.pauseCleaningForNonCompactedPartitions()
} else {
currentLogs.filter {
case (_, log) => !log.config.compact
}
}
}
try {
deletableLogs.foreach {
case (topicPartition, log) =>
debug(s"Garbage collecting '${log.name}'")
total += log.deleteOldSegments()
val futureLog = futureLogs.get(topicPartition)
if (futureLog != null) {
// clean future logs
debug(s"Garbage collecting future log '${futureLog.name}'")
total += futureLog.deleteOldSegments()
}
}
} finally {
if (cleaner != null) {
cleaner.resumeCleaning(deletableLogs.map(_._1))
}
}
debug(s"Log cleanup completed. $total files deleted in " +
(time.milliseconds - startMs) / 1000 + " seconds")
}
/**
* If topic deletion is enabled, delete any log segments that have either expired due to time based retention
* or because the log size is > retentionSize.
*
* Whether or not deletion is enabled, delete any log segments that are before the log start offset
*/
def deleteOldSegments(): Int = {
if (config.delete) {
deleteRetentionMsBreachedSegments() + deleteRetentionSizeBreachedSegments() + deleteLogStartOffsetBreachedSegments()
} else {
deleteLogStartOffsetBreachedSegments()
}
}
// 根据时间策略删除相关日志
private def deleteRetentionMsBreachedSegments(): Int = {
if (config.retentionMs < 0) return 0
val startMs = time.milliseconds
deleteOldSegments((segment, _) => startMs - segment.largestTimestamp > config.retentionMs,
reason = s"retention time ${config.retentionMs}ms breach")
}
// 根据日志大小删除相关日志
private def deleteRetentionSizeBreachedSegments(): Int = {
if (config.retentionSize < 0 || size < config.retentionSize) return 0
var diff = size - config.retentionSize
def shouldDelete(segment: LogSegment, nextSegmentOpt: Option[LogSegment]) = {
if (diff - segment.size >= 0) {
diff -= segment.size
true
} else {
false
}
}
deleteOldSegments(shouldDelete, reason = s"retention size in bytes ${config.retentionSize} breach")
}
private def deleteLogStartOffsetBreachedSegments(): Int = {
def shouldDelete(segment: LogSegment, nextSegmentOpt: Option[LogSegment]) =
nextSegmentOpt.exists(_.baseOffset <= logStartOffset)
deleteOldSegments(shouldDelete, reason = s"log start offset $logStartOffset breach")
}
}
Kafka对于旧日志段的处理方式有两种
- 删除:超过时间或大小阈值的旧 segment,直接进行删除;
- 压缩:不是直接删除日志分段,而是采用合并压缩的方式进行
Kafka删除的检查策略有两种。一种根据时间过期的策略删除过期的日志,一种是根据日志大小来删除太大的日志。
根据时间策略删除相关日志 retention.ms
config.retentionMs取决于配置log.retention.hours默认为168个小时,也就是7天。删除时要注意两点:
- 对于那些大小为0并且是正在使用中的日志段不会被删除
- 如果扫描完发现全部的日志段都过期了,就要马上新生成一个新的日志段来处理后面的消息
- 日志段的删除时异步的,此处只会标记一下,往日志段文件后面加上.delete后缀,然后开启一个定时任务删除文件。定时任务的延迟时间和file.delete.delay.ms有关系。
根据日志大小删除相关日志 retention.bytes
策略的扫描逻辑,通过size-retentionSize算出diff,遍历segment,对于大小超过diff的日志段,就标记删除。然后将diff的值设置为diff-segment.size。当分区目录下只有一个日志段时,无论该日志段多大,都不会被删除。另外,和时间策略一样,这个删除也是异步删除。
日志刷盘
kafka在处理Producer请求时,只是将日志写到缓存。定期检查各个目录,根据刷盘策略执行flush操作。这个任务保证了每隔多久kafka会执行一次刷盘操作。
当距离上次刷盘的时间超过了log.config.flushMs时间就会执行一次刷盘,将缓存中的内容持久化到磁盘。但是kafka官方给刷盘频率设置的默认值是Long的最大值,也就是说,kafka官方的建议是把刷盘操作交给操作系统来控制。
另外,这个刷盘任务这是控制指定时间刷盘一次。kafka还有一个关于刷盘的策略是根据日志的条数来控制刷盘频率的,也就是配置flush.messages。这个配置是在每次写日志完检查的,当kafka处理Producer请求写日志到缓存后,会检查当前的offset和之前记录的offset直接的差值,如果超过配置的值,就执行一次刷盘。不过flush.messages的默认值也是Long的最大值。
class LogManager() {
/**
* Flush any log which has exceeded its flush interval and has unwritten messages.
*/
private def flushDirtyLogs(): Unit = {
debug("Checking for dirty logs to flush...")
for ((topicPartition, log) <- currentLogs.toList ++ futureLogs.toList) {
try {
val timeSinceLastFlush = time.milliseconds - log.lastFlushTime
debug(s"Checking if flush is needed on ${topicPartition.topic} flush interval ${log.config.flushMs}" +
s" last flushed ${log.lastFlushTime} time since last flush: $timeSinceLastFlush")
if(timeSinceLastFlush >= log.config.flushMs)
log.flush
} catch {
case e: Throwable =>
error(s"Error flushing topic ${topicPartition.topic}", e)
}
}
}
}
日志恢复检查点任务
checkpointLogRecoveryOffsets
checkpointLogStartOffsets
class LogManager() {
/**
* Write out the current recovery point for all logs to a text file in the log directory
* to avoid recovering the whole log on startup.
*/
def checkpointLogRecoveryOffsets(): Unit = {
logsByDir.foreach { case (dir, partitionToLogMap) =>
liveLogDirs.find(_.getAbsolutePath.equals(dir)).foreach { f =>
checkpointRecoveryOffsetsAndCleanSnapshot(f, partitionToLogMap.values.toSeq)
}
}
}
/**
* Write out the current log start offset for all logs to a text file in the log directory
* to avoid exposing data that have been deleted by DeleteRecordsRequest
*/
def checkpointLogStartOffsets(): Unit = {
liveLogDirs.foreach(checkpointLogStartOffsetsInDir)
}
}
遍历所有的LogDir,然后将内存中维护的recovery-checkpoint写到log 目录下文件recovery-point-offset-checkpoint 上,避免启动时恢复所有的日志。
recovery-point-offset-checkpoint 表示已经刷写到磁盘的记录
0 // 当前版本
374 // LogDir目录下有多少个partition目录
__consumer_offsets 22 3 // topic partition编号 recovery-checkpoint
topic1 0 45
topic2 0 2
遍历所有的LogDir,然后将start offset 写到log目录下文件replication-offset-checkpoint 上,避免被DeleteRecordsRequest删除的数据暴露
replication-offset-checkpoint 用来存储每个replica的HighWatermark的(high watermark (HW),表示已经被commited的message,HW以下的数据都是各个replicas间同步的,一致的。
0 // 当前版本
274
__consumer_offsets 22 3 // topic partition编号 recovery-checkpoint
topic1 0 45
topic2 0 2
何时刷新recovery-checkpoint?
kafka会在每次flush的时候更新对应Log的recovery-checkpoint。但是由于kafka的定时flush默认是交给操作系统来执行的。所以只有在新建一个新的segment时,以及对partition进行truncate时(如果replica的offset比leader还大,replica就要执行一次truncate,把超出的那些offset砍掉),才会更新recovery-checkpoint。在正常关闭broker,kafka会保证将最新的offset写入recovery-checkpoint文件中。
分区目录删除任务
遍历logsToBeDeleted列表,然后遍历删除元素
class LogManager() {
/**
* Delete logs marked for deletion. Delete all logs for which `currentDefaultConfig.fileDeleteDelayMs`
* has elapsed after the delete was scheduled. Logs for which this interval has not yet elapsed will be
* considered for deletion in the next iteration of `deleteLogs`. The next iteration will be executed
* after the remaining time for the first log that is not deleted. If there are no more `logsToBeDeleted`,
* `deleteLogs` will be executed after `currentDefaultConfig.fileDeleteDelayMs`.
*/
private def deleteLogs(): Unit = {
var nextDelayMs = 0L
try {
def nextDeleteDelayMs: Long = {
if (!logsToBeDeleted.isEmpty) {
val (_, scheduleTimeMs) = logsToBeDeleted.peek()
scheduleTimeMs + currentDefaultConfig.fileDeleteDelayMs - time.milliseconds()
} else
currentDefaultConfig.fileDeleteDelayMs
}
while ({nextDelayMs = nextDeleteDelayMs; nextDelayMs <= 0}) {
val (removedLog, _) = logsToBeDeleted.take()
if (removedLog != null) {
try {
removedLog.delete()
info(s"Deleted log for partition ${removedLog.topicPartition} in ${removedLog.dir.getAbsolutePath}.")
} catch {
case e: KafkaStorageException =>
error(s"Exception while deleting $removedLog in dir ${removedLog.dir.getParent}.", e)
}
}
}
} catch {
case e: Throwable =>
error(s"Exception in kafka-delete-logs thread.", e)
} finally {
try {
scheduler.schedule("kafka-delete-logs",
deleteLogs _,
delay = nextDelayMs,
unit = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
} catch {
case e: Throwable =>
if (scheduler.isStarted) {
// No errors should occur unless scheduler has been shutdown
error(s"Failed to schedule next delete in kafka-delete-logs thread", e)
}
}
}
}
/**
* 异步删除
* Rename the directory of the given topic-partition "logdir" as "logdir.uuid.delete" and
* add it in the queue for deletion.
*
* @param topicPartition TopicPartition that needs to be deleted
* @param isFuture True iff the future log of the specified partition should be deleted
* @return the removed log
*/
def asyncDelete(topicPartition: TopicPartition, isFuture: Boolean = false): Log = {
val removedLog: Log = logCreationOrDeletionLock synchronized {
if (isFuture)
futureLogs.remove(topicPartition)
else
currentLogs.remove(topicPartition)
}
if (removedLog != null) {
//We need to wait until there is no more cleaning task on the log to be deleted before actually deleting it.
if (cleaner != null && !isFuture) {
cleaner.abortCleaning(topicPartition)
cleaner.updateCheckpoints(removedLog.dir.getParentFile)
}
removedLog.renameDir(Log.logDeleteDirName(topicPartition))
checkpointRecoveryOffsetsAndCleanSnapshot(removedLog.dir.getParentFile, ArrayBuffer.empty)
checkpointLogStartOffsetsInDir(removedLog.dir.getParentFile)
addLogToBeDeleted(removedLog)
info(s"Log for partition ${removedLog.topicPartition} is renamed to ${removedLog.dir.getAbsolutePath} and is scheduled for deletion")
} else if (offlineLogDirs.nonEmpty) {
throw new KafkaStorageException(s"Failed to delete log for ${if (isFuture) "future" else ""} $topicPartition because it may be in one of the offline directories ${offlineLogDirs.mkString(",")}")
}
removedLog
}
}
那么什么时候分区会被加到logsToBeDeleted中待删除呢?
LogManager启动时会扫描所有分区目录名结尾是-delete的分区,加入到logsToBeDeleted中。分区被删除的时候走的都是异步删除策略,会先被加入到logsToBeDeleted中等待删除。在kafka中,要删除分区需要往broker发送StopReplica请求。broker收到StopReplica请求后,判断是否需要删除分区,如果要删除就执行异步删除。
异步删除
- 需要先把分区目录标记一下,在后缀加上-delete表示该分区准备删除了。这样做可以防止如果删除时间没到就宕机,下次重启时可以扫描-delete结尾的分区再删除
- 把分区目录添加到logsToBeDeleted中待删除
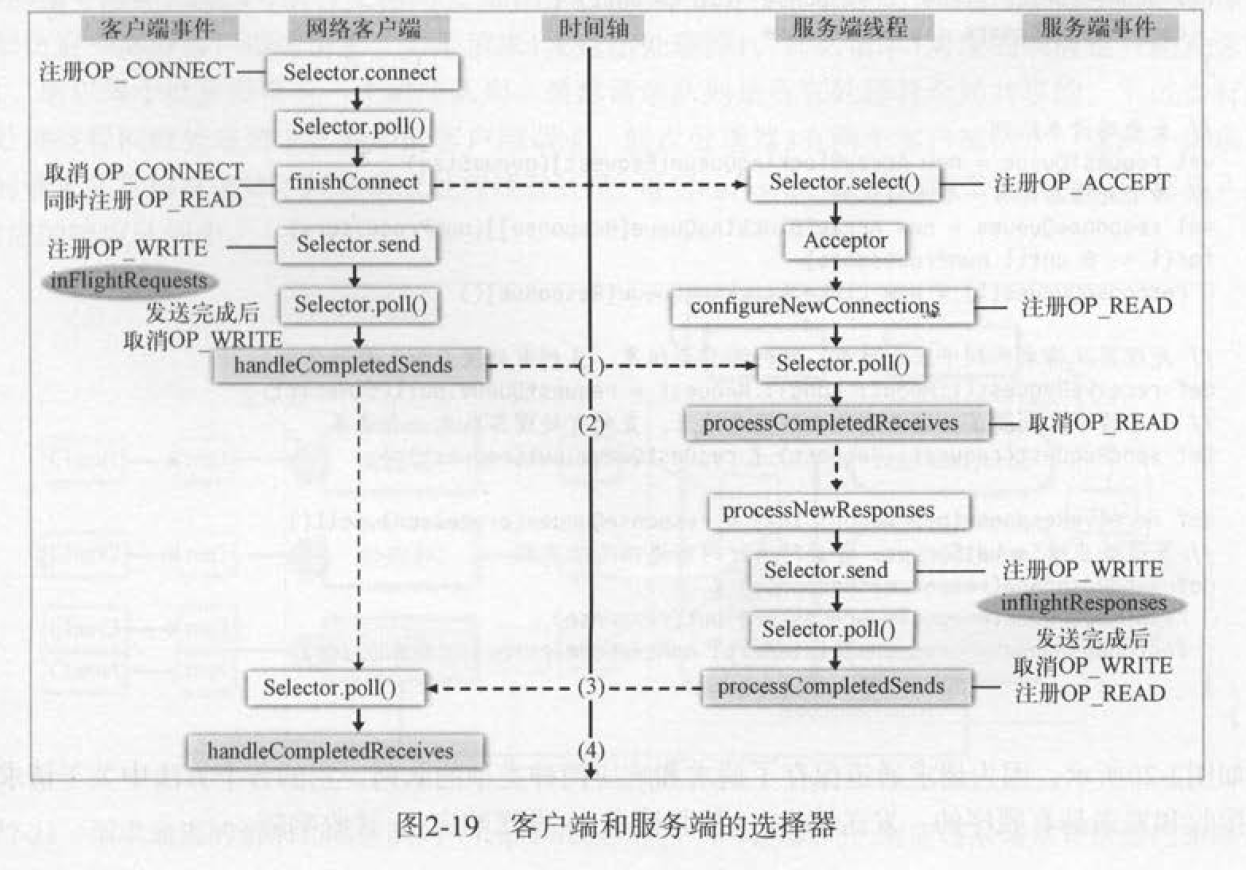
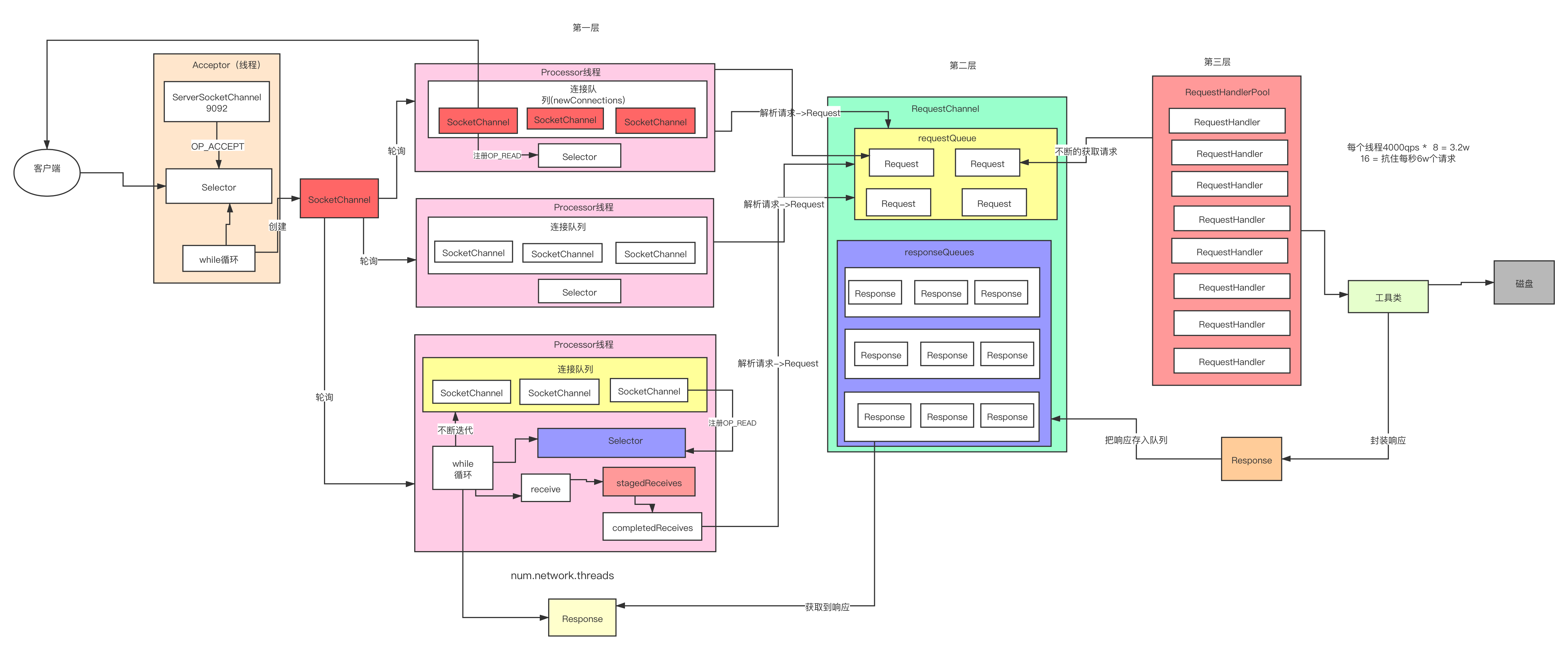
SocketServer
KafkaServer 通过 SocketServer 接受消息并且进行处理。并采用了 Reactor 模式。
SocketServer是socket服务器。线程模型是:1个Acceptor线程处理新连接,Acceptor还有多个处理器线程,每个处理器线程拥有自己的选择器和多个读socket请求Handler线程。handler线程处理请求并产生响应写给处理器线程。
Reactor 网络通信模型
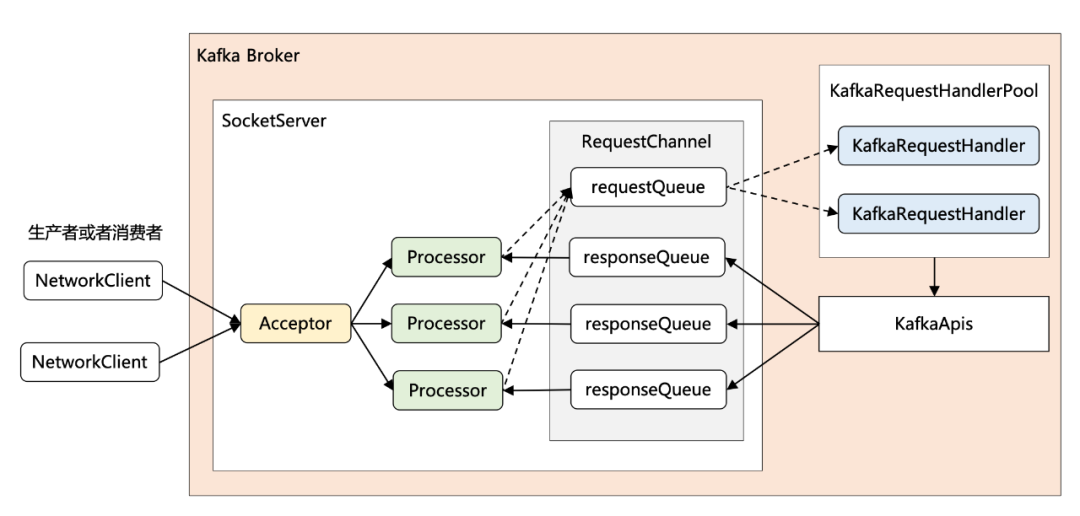
1 + N + M
- 1:表示 1 个 Acceptor 线程,负责监听新的连接,然后将新连接交给 Processor 线程处理
- N:表示 N 个 Processor 线程,每个 Processor 都有自己的 selector,负责从 socket 中读写数据。
- M:表示 M 个 KafkaRequestHandler 业务处理线程,它通过调用 KafkaApis 进行业务处理,然后生成 response,再交由给 Processor 线程。
/**
* Handles new connections, requests and responses to and from broker.
* Kafka supports two types of request planes :
* - data-plane :
* - Handles requests from clients and other brokers in the cluster.
* - The threading model is
* 1 Acceptor thread per listener, that handles new connections.
* It is possible to configure multiple data-planes by specifying multiple "," separated endpoints for "listeners" in KafkaConfig.
* Acceptor has N Processor threads that each have their own selector and read requests from sockets
* M Handler threads that handle requests and produce responses back to the processor threads for writing.
* - control-plane :
* - Handles requests from controller. This is optional and can be configured by specifying "control.plane.listener.name".
* If not configured, the controller requests are handled by the data-plane.
* - The threading model is
* 1 Acceptor thread that handles new connections
* Acceptor has 1 Processor thread that has its own selector and read requests from the socket.
* 1 Handler thread that handles requests and produce responses back to the processor thread for writing.
*/
class SocketServer() {
private val maxQueuedRequests = config.queuedMaxRequests
// data-plane
private val dataPlaneProcessors = new ConcurrentHashMap[Int, Processor]()
private[network] val dataPlaneAcceptors = new ConcurrentHashMap[EndPoint, Acceptor]()
// RequestChannel负责消息从网络层转接到业务层,以及将业务层的处理结果交付给网络层进而返回给客户端。
val dataPlaneRequestChannel = new RequestChannel(maxQueuedRequests, DataPlaneMetricPrefix)
// control-plane
private var controlPlaneProcessorOpt : Option[Processor] = None
private[network] var controlPlaneAcceptorOpt : Option[Acceptor] = None
val controlPlaneRequestChannelOpt: Option[RequestChannel] = config.controlPlaneListenerName.map(_ => new RequestChannel(20, ControlPlaneMetricPrefix))
def startup(startupProcessors: Boolean = true): Unit = {
this.synchronized {
// 控制每个 ip 上最大的连接数的
connectionQuotas = new ConnectionQuotas(config, time)
// 创建 Acceptor 和 Processor
createControlPlaneAcceptorAndProcessor(config.controlPlaneListener)
createDataPlaneAcceptorsAndProcessors(config.numNetworkThreads, config.dataPlaneListeners)
// 开启 processor 线程
if (startupProcessors) {
startControlPlaneProcessor(Map.empty)
startDataPlaneProcessors(Map.empty)
}
}
...
info(s"Started ${dataPlaneAcceptors.size} acceptor threads for data-plane")
if (controlPlaneAcceptorOpt.isDefined)
info("Started control-plane acceptor thread")
}
private def endpoints = config.listeners.map(l => l.listenerName -> l).toMap
private def createDataPlaneAcceptorsAndProcessors(dataProcessorsPerListener: Int,
endpoints: Seq[EndPoint]): Unit = synchronized {
// 每一个endPoint创建一个Acceptor,创建多个Processor放入processor线程数组
endpoints.foreach { endpoint =>
connectionQuotas.addListener(config, endpoint.listenerName)
val dataPlaneAcceptor = createAcceptor(endpoint, DataPlaneMetricPrefix)
addDataPlaneProcessors(dataPlaneAcceptor, endpoint, dataProcessorsPerListener)
KafkaThread.nonDaemon(s"data-plane-kafka-socket-acceptor-${endpoint.listenerName}-${endpoint.securityProtocol}-${endpoint.port}", dataPlaneAcceptor).start()
dataPlaneAcceptor.awaitStartup()
dataPlaneAcceptors.put(endpoint, dataPlaneAcceptor)
info(s"Created data-plane acceptor and processors for endpoint : $endpoint")
}
}
private def createControlPlaneAcceptorAndProcessor(endpointOpt: Option[EndPoint]): Unit = synchronized {
endpointOpt.foreach { endpoint =>
connectionQuotas.addListener(config, endpoint.listenerName)
// Acceptor
val controlPlaneAcceptor = createAcceptor(endpoint, ControlPlaneMetricPrefix)
val controlPlaneProcessor = newProcessor(nextProcessorId, controlPlaneRequestChannelOpt.get, connectionQuotas, endpoint.listenerName, endpoint.securityProtocol, memoryPool)
controlPlaneAcceptorOpt = Some(controlPlaneAcceptor)
controlPlaneProcessorOpt = Some(controlPlaneProcessor)
val listenerProcessors = new ArrayBuffer[Processor]()
listenerProcessors += controlPlaneProcessor
controlPlaneRequestChannelOpt.foreach(_.addProcessor(controlPlaneProcessor))
nextProcessorId += 1
// Processors
controlPlaneAcceptor.addProcessors(listenerProcessors, ControlPlaneThreadPrefix)
// 创建非守护进程
KafkaThread.nonDaemon(s"${ControlPlaneThreadPrefix}-kafka-socket-acceptor-${endpoint.listenerName}-${endpoint.securityProtocol}-${endpoint.port}", controlPlaneAcceptor).start()
controlPlaneAcceptor.awaitStartup()
info(s"Created control-plane acceptor and processor for endpoint : $endpoint")
}
}
private def createAcceptor(endPoint: EndPoint, metricPrefix: String) : Acceptor = synchronized {
val sendBufferSize = config.socketSendBufferBytes
val recvBufferSize = config.socketReceiveBufferBytes
val brokerId = config.brokerId
new Acceptor(endPoint, sendBufferSize, recvBufferSize, brokerId, connectionQuotas, metricPrefix)
}
}
// openServerSocket()打开对应的EndPoint的Socket,即打开端口并启动监听。
// run()方法处理op_accept 事件创建 socketChannel 并调用 accept方法,accept 方法则是把该事件交给 Processor.accept 处理
private[kafka] class Acceptor() {
private val nioSelector = NSelector.open()
val serverChannel = openServerSocket(endPoint.host, endPoint.port)
// Acceptor会负责构造并管理的一个Processor的ArrayBuffer,每一个Processor都是一个独立线程
private val processors = new ArrayBuffer[Processor]()
private val processorsStarted = new AtomicBoolean
private[network] def addProcessors(newProcessors: Buffer[Processor], processorThreadPrefix: String): Unit = synchronized {
processors ++= newProcessors
if (processorsStarted.get)
startProcessors(newProcessors, processorThreadPrefix)
}
private[network] def startProcessors(processorThreadPrefix: String): Unit = synchronized {
if (!processorsStarted.getAndSet(true)) {
startProcessors(processors, processorThreadPrefix)
}
}
private def startProcessors(processors: Seq[Processor], processorThreadPrefix: String): Unit = synchronized {
processors.foreach { processor =>
KafkaThread.nonDaemon(s"${processorThreadPrefix}-kafka-network-thread-$brokerId-${endPoint.listenerName}-${endPoint.securityProtocol}-${processor.id}",
processor).start()
}
}
// 不断监听对应ServerChannel上的连接请求(ACCEPT),如果有新的连接请求,使用的轮询方式将通道分配给Processor
// 调用assignNewConnection把新连接交付给Processor
def run(): Unit = {
// 注册nio的OP_ACCEPT
serverChannel.register(nioSelector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)
// 标记当前线程已经启动,唤醒阻塞线程
startupComplete()
try {
var currentProcessorIndex = 0
// 线程存活,执行
while (isRunning) {
try {
// nioSelector
// 等待nio关注事件,等待时间500ms
val ready = nioSelector.select(500)
if (ready > 0) {
val keys = nioSelector.selectedKeys()
val iter = keys.iterator()
while (iter.hasNext && isRunning) {
try {
val key = iter.next
iter.remove()
if (key.isAcceptable) {
accept(key).foreach { socketChannel =>
// 轮询方式选择 processor
// Assign the channel to the next processor (using round-robin) to which the
// channel can be added without blocking. If newConnections queue is full on
// all processors, block until the last one is able to accept a connection.
var retriesLeft = synchronized(processors.length)
var processor: Processor = null
do {
retriesLeft -= 1
processor = synchronized {
// adjust the index (if necessary) and retrieve the processor atomically for
// correct behaviour in case the number of processors is reduced dynamically
currentProcessorIndex = currentProcessorIndex % processors.length
processors(currentProcessorIndex)
}
currentProcessorIndex += 1
} while (!assignNewConnection(socketChannel, processor, retriesLeft == 0))
}
} else
throw new IllegalStateException("Unrecognized key state for acceptor thread.")
} catch {
case e: Throwable => error("Error while accepting connection", e)
}
}
}
}
catch {
...
}
}
} finally {
debug("Closing server socket and selector.")
CoreUtils.swallow(serverChannel.close(), this, Level.ERROR)
CoreUtils.swallow(nioSelector.close(), this, Level.ERROR)
shutdownComplete()
}
}
/**
* Create a server socket to listen for connections on.
*/
private def openServerSocket(host: String, port: Int): ServerSocketChannel = {
val socketAddress =
if (host == null || host.trim.isEmpty)
new InetSocketAddress(port)
else
new InetSocketAddress(host, port)
val serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open()
serverChannel.configureBlocking(false)
if (recvBufferSize != Selectable.USE_DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE)
serverChannel.socket().setReceiveBufferSize(recvBufferSize)
try {
serverChannel.socket.bind(socketAddress)
info(s"Awaiting socket connections on ${socketAddress.getHostString}:${serverChannel.socket.getLocalPort}.")
} catch {
case e: SocketException =>
throw new KafkaException(s"Socket server failed to bind to ${socketAddress.getHostString}:$port: ${e.getMessage}.", e)
}
serverChannel
}
// assignNewConnection中通过processor.accept的调用,将SocketChannel放入每个processor维护的新连接的队列,后面processor会从队列取出做后续处理
private def assignNewConnection(socketChannel: SocketChannel, processor: Processor, mayBlock: Boolean): Boolean = {
if (processor.accept(socketChannel, mayBlock, blockedPercentMeter)) {
true
} else
false
}
}
Processor:核心方法是 run 方法,调用 poll 方法发送成功后会加入 completedReceives,conpletedSends,disConnected 中等待处理。
每一个SocketServer只有一个RequestChannel对象,在SocketServer中构造。RequestChannel构造方法中初始化了requestQueue,用来存放网络层接收到的请求,这些请求即将交付给业务层进行处理。同时,初始化了responseQueues,为每一个Processor建立了一个response队列,用来存放这个Processor的一个或者多个Response,这些response即将交付给网络层返回给客户端。
Processor.processCompletedReceives()通过遍历completedReceives,对于每一个已经完成接收的数据,对数据进行解析和封装,交付给RequestChannel,RequestChannel会交付给具体的业务处理层进行处理。其中RequestChannel拿到请求数据,会调用RequestChannel.sendRequest方法,将请求put到requestQueue中,以供后续的处理请求线程处理。
private[kafka] object Processor {
val IdlePercentMetricName = "IdlePercent"
val NetworkProcessorMetricTag = "networkProcessor"
val ListenerMetricTag = "listener"
val ConnectionQueueSize = 20
}
/**
* Thread that processes all requests from a single connection. There are N of these running in parallel
* each of which has its own selector
*/
private[kafka] class Processor(val id: Int,
time: Time,
maxRequestSize: Int,
requestChannel: RequestChannel,
connectionQuotas: ConnectionQuotas,
connectionsMaxIdleMs: Long,
failedAuthenticationDelayMs: Int,
listenerName: ListenerName,
securityProtocol: SecurityProtocol,
config: KafkaConfig,
metrics: Metrics,
credentialProvider: CredentialProvider,
memoryPool: MemoryPool,
logContext: LogContext,
connectionQueueSize: Int = ConnectionQueueSize) extends AbstractServerThread(connectionQuotas) with KafkaMetricsGroup {
// 维护一个新连接队列,在run方法里会取出处理
private val newConnections = new ArrayBlockingQueue[SocketChannel](connectionQueueSize)
private val inflightResponses = mutable.Map[String, RequestChannel.Response]()
// 每一个processor维护一个responseQueue
private val responseQueue = new LinkedBlockingDeque[RequestChannel.Response]()
// processor都维护了一个单独的Selector
private val selector = createSelector(
ChannelBuilders.serverChannelBuilder(listenerName,
listenerName == config.interBrokerListenerName,
securityProtocol,
config,
credentialProvider.credentialCache,
credentialProvider.tokenCache,
time))
// Visible to override for testing
protected[network] def createSelector(channelBuilder: ChannelBuilder): KSelector = {
channelBuilder match {
case reconfigurable: Reconfigurable => config.addReconfigurable(reconfigurable)
case _ =>
}
new KSelector(
maxRequestSize,
connectionsMaxIdleMs,
failedAuthenticationDelayMs,
metrics,
time,
"socket-server",
metricTags,
false,
true,
channelBuilder,
memoryPool,
logContext)
}
// Connection ids have the format `localAddr:localPort-remoteAddr:remotePort-index`. The index is a
// non-negative incrementing value that ensures that even if remotePort is reused after a connection is
// closed, connection ids are not reused while requests from the closed connection are being processed.
private var nextConnectionIndex = 0
override def run(): Unit = {
startupComplete()
try {
while (isRunning) {
try {
// setup any new connections that have been queued up
// processor从newConnections队列取出新连接,并将其注册到selector并监听OR_READ事件
configureNewConnections()
// register any new responses for writing
// 处理响应队列,这个响应队列是Handler线程处理以后的结果,会交付给RequestChannel.responseQueue.同时调用unmute,开始接受请求
processNewResponses()
// 调用KSelector.poll(),进行真正的数据读写
poll()
// 调用Selector.mute,不再接受Read请求,发送响应之前,不可以再接收任何请求
processCompletedReceives()
processCompletedSends()
processDisconnected()
closeExcessConnections()
} catch {
...
}
}
} finally {
...
}
}
private def processNewResponses(): Unit = {
var currentResponse: RequestChannel.Response = null
while ({currentResponse = dequeueResponse(); currentResponse != null}) {
val channelId = currentResponse.request.context.connectionId
try {
currentResponse match {
case response: NoOpResponse =>
// There is no response to send to the client, we need to read more pipelined requests
// that are sitting in the server's socket buffer
updateRequestMetrics(response)
trace(s"Socket server received empty response to send, registering for read: $response")
// Try unmuting the channel. If there was no quota violation and the channel has not been throttled,
// it will be unmuted immediately. If the channel has been throttled, it will be unmuted only if the
// throttling delay has already passed by now.
handleChannelMuteEvent(channelId, ChannelMuteEvent.RESPONSE_SENT)
tryUnmuteChannel(channelId)
case response: SendResponse =>
sendResponse(response, response.responseSend)
case response: CloseConnectionResponse =>
updateRequestMetrics(response)
trace("Closing socket connection actively according to the response code.")
close(channelId)
case _: StartThrottlingResponse =>
handleChannelMuteEvent(channelId, ChannelMuteEvent.THROTTLE_STARTED)
case _: EndThrottlingResponse =>
// Try unmuting the channel. The channel will be unmuted only if the response has already been sent out to
// the client.
handleChannelMuteEvent(channelId, ChannelMuteEvent.THROTTLE_ENDED)
tryUnmuteChannel(channelId)
case _ =>
throw new IllegalArgumentException(s"Unknown response type: ${currentResponse.getClass}")
}
} catch {
case e: Throwable =>
processChannelException(channelId, s"Exception while processing response for $channelId", e)
}
}
}
private def poll(): Unit = {
val pollTimeout = if (newConnections.isEmpty) 300 else 0
try selector.poll(pollTimeout)
catch {
case e @ (_: IllegalStateException | _: IOException) =>
// The exception is not re-thrown and any completed sends/receives/connections/disconnections
// from this poll will be processed.
error(s"Processor $id poll failed", e)
}
}
private def processCompletedReceives(): Unit = {
selector.completedReceives.asScala.foreach { receive =>
try {
openOrClosingChannel(receive.source) match {
case Some(channel) =>
val header = RequestHeader.parse(receive.payload)
if (header.apiKey() == ApiKeys.SASL_HANDSHAKE && channel.maybeBeginServerReauthentication(receive, nowNanosSupplier))
trace(s"Begin re-authentication: $channel")
else {
val nowNanos = time.nanoseconds()
if (channel.serverAuthenticationSessionExpired(nowNanos)) {
// be sure to decrease connection count and drop any in-flight responses
debug(s"Disconnecting expired channel: $channel : $header")
close(channel.id)
expiredConnectionsKilledCount.record(null, 1, 0)
} else {
val connectionId = receive.source
val context = new RequestContext(header, connectionId, channel.socketAddress,
channel.principal, listenerName, securityProtocol)
val req = new RequestChannel.Request(processor = id, context = context,
startTimeNanos = nowNanos, memoryPool, receive.payload, requestChannel.metrics)
// 将请求通过RequestChannel.requestQueue交付给Handler
requestChannel.sendRequest(req)
// 不再接受Read请求发送响应之前,不可以再接收任何请求
selector.mute(connectionId)
handleChannelMuteEvent(connectionId, ChannelMuteEvent.REQUEST_RECEIVED)
}
}
case None =>
// This should never happen since completed receives are processed immediately after `poll()`
throw new IllegalStateException(s"Channel ${receive.source} removed from selector before processing completed receive")
}
} catch {
...
}
}
}
private def processCompletedSends(): Unit = {
selector.completedSends.asScala.foreach { send =>
try {
val response = inflightResponses.remove(send.destination).getOrElse {
throw new IllegalStateException(s"Send for ${send.destination} completed, but not in `inflightResponses`")
}
updateRequestMetrics(response)
// Invoke send completion callback
response.onComplete.foreach(onComplete => onComplete(send))
// Try unmuting the channel. If there was no quota violation and the channel has not been throttled,
// it will be unmuted immediately. If the channel has been throttled, it will unmuted only if the throttling
// delay has already passed by now.
handleChannelMuteEvent(send.destination, ChannelMuteEvent.RESPONSE_SENT)
tryUnmuteChannel(send.destination)
} catch {
case e: Throwable => processChannelException(send.destination,
s"Exception while processing completed send to ${send.destination}", e)
}
}
}
/**
* 放入队列 newConnections
* Queue up a new connection for reading
*/
def accept(socketChannel: SocketChannel,
mayBlock: Boolean,
acceptorIdlePercentMeter: com.yammer.metrics.core.Meter): Boolean = {
val accepted = {
if (newConnections.offer(socketChannel))
true
else if (mayBlock) {
val startNs = time.nanoseconds
newConnections.put(socketChannel)
acceptorIdlePercentMeter.mark(time.nanoseconds() - startNs)
true
} else
false
}
if (accepted)
wakeup()
accepted
}
private def configureNewConnections(): Unit = {
var connectionsProcessed = 0
while (connectionsProcessed < connectionQueueSize && !newConnections.isEmpty) {
// 取出新连接SocketChannel
val channel = newConnections.poll()
try {
// 将SocketChannel注册到selector OP_READ
selector.register(connectionId(channel.socket), channel)
connectionsProcessed += 1
} catch {
...
}
}
}
/**
* Wakeup the thread for selection.
*/
override def wakeup() = selector.wakeup()
}
public class Selector {
public void register(String id, SocketChannel socketChannel) throws IOException {
ensureNotRegistered(id);
registerChannel(id, socketChannel, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
this.sensors.connectionCreated.record();
}
}
KafkaApis
KafkaApis 是 kafka 服务器处理请求的入口,它负责将请求分发到不同的 handle*() 进行处理
48个API
class KafkaApis() {
/**
* Top-level method that handles all requests and multiplexes to the right api
*/
def handle(request: RequestChannel.Request): Unit = {
try {
trace(s"Handling request:${request.requestDesc(true)} from connection ${request.context.connectionId};" +
s"securityProtocol:${request.context.securityProtocol},principal:${request.context.principal}")
request.header.apiKey match {
case ApiKeys.PRODUCE => handleProduceRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.FETCH => handleFetchRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.LIST_OFFSETS => handleListOffsetRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.METADATA => handleTopicMetadataRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.LEADER_AND_ISR => handleLeaderAndIsrRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.STOP_REPLICA => handleStopReplicaRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.UPDATE_METADATA => handleUpdateMetadataRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.CONTROLLED_SHUTDOWN => handleControlledShutdownRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.OFFSET_COMMIT => handleOffsetCommitRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.OFFSET_FETCH => handleOffsetFetchRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.FIND_COORDINATOR => handleFindCoordinatorRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.JOIN_GROUP => handleJoinGroupRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.HEARTBEAT => handleHeartbeatRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.LEAVE_GROUP => handleLeaveGroupRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.SYNC_GROUP => handleSyncGroupRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.DESCRIBE_GROUPS => handleDescribeGroupRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.LIST_GROUPS => handleListGroupsRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.SASL_HANDSHAKE => handleSaslHandshakeRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.API_VERSIONS => handleApiVersionsRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.CREATE_TOPICS => handleCreateTopicsRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.DELETE_TOPICS => handleDeleteTopicsRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.DELETE_RECORDS => handleDeleteRecordsRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.INIT_PRODUCER_ID => handleInitProducerIdRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.OFFSET_FOR_LEADER_EPOCH => handleOffsetForLeaderEpochRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.ADD_PARTITIONS_TO_TXN => handleAddPartitionToTxnRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.ADD_OFFSETS_TO_TXN => handleAddOffsetsToTxnRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.END_TXN => handleEndTxnRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.WRITE_TXN_MARKERS => handleWriteTxnMarkersRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.TXN_OFFSET_COMMIT => handleTxnOffsetCommitRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.DESCRIBE_ACLS => handleDescribeAcls(request)
case ApiKeys.CREATE_ACLS => handleCreateAcls(request)
case ApiKeys.DELETE_ACLS => handleDeleteAcls(request)
case ApiKeys.ALTER_CONFIGS => handleAlterConfigsRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.DESCRIBE_CONFIGS => handleDescribeConfigsRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.ALTER_REPLICA_LOG_DIRS => handleAlterReplicaLogDirsRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.DESCRIBE_LOG_DIRS => handleDescribeLogDirsRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.SASL_AUTHENTICATE => handleSaslAuthenticateRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.CREATE_PARTITIONS => handleCreatePartitionsRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.CREATE_DELEGATION_TOKEN => handleCreateTokenRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.RENEW_DELEGATION_TOKEN => handleRenewTokenRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.EXPIRE_DELEGATION_TOKEN => handleExpireTokenRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.DESCRIBE_DELEGATION_TOKEN => handleDescribeTokensRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.DELETE_GROUPS => handleDeleteGroupsRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.ELECT_LEADERS => handleElectReplicaLeader(request)
case ApiKeys.INCREMENTAL_ALTER_CONFIGS => handleIncrementalAlterConfigsRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.ALTER_PARTITION_REASSIGNMENTS => handleAlterPartitionReassignmentsRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.LIST_PARTITION_REASSIGNMENTS => handleListPartitionReassignmentsRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.OFFSET_DELETE => handleOffsetDeleteRequest(request)
}
} catch {
case e: FatalExitError => throw e
case e: Throwable => handleError(request, e)
} finally {
request.apiLocalCompleteTimeNanos = time.nanoseconds
}
}
/**
* Handle a produce request
*/
def handleProduceRequest(request: RequestChannel.Request): Unit = {
val produceRequest = request.body[ProduceRequest]
val numBytesAppended = request.header.toStruct.sizeOf + request.sizeOfBodyInBytes
if (produceRequest.hasTransactionalRecords) {
val isAuthorizedTransactional = produceRequest.transactionalId != null &&
authorize(request, WRITE, TRANSACTIONAL_ID, produceRequest.transactionalId)
if (!isAuthorizedTransactional) {
sendErrorResponseMaybeThrottle(request, Errors.TRANSACTIONAL_ID_AUTHORIZATION_FAILED.exception)
return
}
// Note that authorization to a transactionalId implies ProducerId authorization
} else if (produceRequest.hasIdempotentRecords && !authorize(request, IDEMPOTENT_WRITE, CLUSTER, CLUSTER_NAME)) {
sendErrorResponseMaybeThrottle(request, Errors.CLUSTER_AUTHORIZATION_FAILED.exception)
return
}
val unauthorizedTopicResponses = mutable.Map[TopicPartition, PartitionResponse]()
val nonExistingTopicResponses = mutable.Map[TopicPartition, PartitionResponse]()
val invalidRequestResponses = mutable.Map[TopicPartition, PartitionResponse]()
val authorizedRequestInfo = mutable.Map[TopicPartition, MemoryRecords]()
val authorizedTopics = filterAuthorized(request, WRITE, TOPIC,
produceRequest.partitionRecordsOrFail.asScala.toSeq.map(_._1.topic))
// 遍历这个ProduceRequest 本次发送过来的所有消息记录。对ProduceRequest 中所有Record 的处理是逐条处理的,并不是某一条的异常影响所有Record 都失败
for ((topicPartition, memoryRecords) <- produceRequest.partitionRecordsOrFail.asScala) {
// 如果判断topic未授权,生成未授权topic 的response
if (!authorizedTopics.contains(topicPartition.topic))
unauthorizedTopicResponses += topicPartition -> new PartitionResponse(Errors.TOPIC_AUTHORIZATION_FAILED)
else if (!metadataCache.contains(topicPartition))
// 如果判断broker的元数据缓存不包含该topicPartition,生成不存在topic的response
nonExistingTopicResponses += topicPartition -> new PartitionResponse(Errors.UNKNOWN_TOPIC_OR_PARTITION)
else
// 如果brocker的元数据缓存包含该topicPartition,将该二元组添加到authorizedRequestInfo的map集合
try {
ProduceRequest.validateRecords(request.header.apiVersion(), memoryRecords)
authorizedRequestInfo += (topicPartition -> memoryRecords)
} catch {
case e: ApiException =>
invalidRequestResponses += topicPartition -> new PartitionResponse(Errors.forException(e))
}
}
// 处理完所有请求后,回调该函数返回应答
// the callback for sending a produce response
def sendResponseCallback(responseStatus: Map[TopicPartition, PartitionResponse]): Unit = {
val mergedResponseStatus = responseStatus ++ unauthorizedTopicResponses ++ nonExistingTopicResponses ++ invalidRequestResponses
var errorInResponse = false
// 逐个处理应答
mergedResponseStatus.foreach { case (topicPartition, status) =>
if (status.error != Errors.NONE) {
errorInResponse = true
debug("Produce request with correlation id %d from client %s on partition %s failed due to %s".format(
request.header.correlationId,
request.header.clientId,
topicPartition,
status.error.exceptionName))
}
}
// When this callback is triggered, the remote API call has completed
request.apiRemoteCompleteTimeNanos = time.nanoseconds
// Record both bandwidth and request quota-specific values and throttle by muting the channel if any of the quotas
// have been violated. If both quotas have been violated, use the max throttle time between the two quotas. Note
// that the request quota is not enforced if acks == 0.
val bandwidthThrottleTimeMs = quotas.produce.maybeRecordAndGetThrottleTimeMs(request, numBytesAppended, time.milliseconds())
val requestThrottleTimeMs = if (produceRequest.acks == 0) 0 else quotas.request.maybeRecordAndGetThrottleTimeMs(request)
val maxThrottleTimeMs = Math.max(bandwidthThrottleTimeMs, requestThrottleTimeMs)
if (maxThrottleTimeMs > 0) {
if (bandwidthThrottleTimeMs > requestThrottleTimeMs) {
quotas.produce.throttle(request, bandwidthThrottleTimeMs, sendResponse)
} else {
quotas.request.throttle(request, requestThrottleTimeMs, sendResponse)
}
}
// Send the response immediately. In case of throttling, the channel has already been muted.
if (produceRequest.acks == 0) {
// no operation needed if producer request.required.acks = 0; however, if there is any error in handling
// the request, since no response is expected by the producer, the server will close socket server so that
// the producer client will know that some error has happened and will refresh its metadata
if (errorInResponse) {
val exceptionsSummary = mergedResponseStatus.map { case (topicPartition, status) =>
topicPartition -> status.error.exceptionName
}.mkString(", ")
info(
s"Closing connection due to error during produce request with correlation id ${request.header.correlationId} " +
s"from client id ${request.header.clientId} with ack=0\n" +
s"Topic and partition to exceptions: $exceptionsSummary"
)
closeConnection(request, new ProduceResponse(mergedResponseStatus.asJava).errorCounts)
} else {
// Note that although request throttling is exempt for acks == 0, the channel may be throttled due to
// bandwidth quota violation.
sendNoOpResponseExemptThrottle(request)
}
} else {
sendResponse(request, Some(new ProduceResponse(mergedResponseStatus.asJava, maxThrottleTimeMs)), None)
}
}
def processingStatsCallback(processingStats: FetchResponseStats): Unit = {
processingStats.foreach { case (tp, info) =>
updateRecordConversionStats(request, tp, info)
}
}
if (authorizedRequestInfo.isEmpty)
sendResponseCallback(Map.empty)
else {
val internalTopicsAllowed = request.header.clientId == AdminUtils.AdminClientId
// 调用副本管理的方法,将消息添加到对应所有的副本分区中。将record添加到副本broker
// call the replica manager to append messages to the replicas
replicaManager.appendRecords(
timeout = produceRequest.timeout.toLong,
requiredAcks = produceRequest.acks,
internalTopicsAllowed = internalTopicsAllowed,
origin = AppendOrigin.Client,
entriesPerPartition = authorizedRequestInfo,
responseCallback = sendResponseCallback,
recordConversionStatsCallback = processingStatsCallback)
// if the request is put into the purgatory, it will have a held reference and hence cannot be garbage collected;
// hence we clear its data here in order to let GC reclaim its memory since it is already appended to log
produceRequest.clearPartitionRecords()
}
}
}
KafkaRequestHandler
KafkaRequestHandlerPool 处理request的线程池,请求处理池。KafkaRequestHandlerPool构造方法中初始化并启动了多个KafkaRequestHandler线程对象,线程池大小通过Kafka配置文件配置项num.io.threads进行配置。KafkaRequestHandlerPool线程池中的所有KafkaRequestHandler,通过竞争方式从RequestChannel.requestQueue中获取请求进行处理。由于requestQueue的类型是ArrayBlockingQueue,通过调用ArrayBlockingQueue.poll()方法取出请求.
KafkaRequestHandler 请求处理线程
KafkaRequestHandler run方法的具体逻辑是从RequestChannel取出processor之前put请求,调用KafkaApi针对不同请求类型分别处理
ApiKeys.PRODUCE,handleProduceRequest方法中有两个重要的方法sendResponseCallback()和replicaManager.appendRecords(),sendResponseCallback回调函数中调用requestChannel.sendResponse()将response交付给RequestChannel。replicaManager.appendRecords。
class KafkaRequestHandlerPool() {
private val threadPoolSize: AtomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(numThreads)
val runnables = new mutable.ArrayBuffer[KafkaRequestHandler](numThreads)
for (i <- 0 until numThreads) {
createHandler(i)
}
def createHandler(id: Int): Unit = synchronized {
runnables += new KafkaRequestHandler(id, brokerId, aggregateIdleMeter, threadPoolSize, requestChannel, apis, time)
KafkaThread.daemon(logAndThreadNamePrefix + "-kafka-request-handler-" + id, runnables(id)).start()
}
}
class KafkaRequestHandler() {
def run(): Unit = {
while (!stopped) {
// We use a single meter for aggregate idle percentage for the thread pool.
// Since meter is calculated as total_recorded_value / time_window and
// time_window is independent of the number of threads, each recorded idle
// time should be discounted by # threads.
val startSelectTime = time.nanoseconds
// 从RequestChannel.requestQueue队列中取出请求
val req = requestChannel.receiveRequest(300)
val endTime = time.nanoseconds
// 统计线程空闲时间
val idleTime = endTime - startSelectTime
aggregateIdleMeter.mark(idleTime / totalHandlerThreads.get)
req match {
// 关闭线程请求,说明该 Broker 发起了关闭操作
case RequestChannel.ShutdownRequest =>
debug(s"Kafka request handler $id on broker $brokerId received shut down command")
shutdownComplete.countDown()
return
// 普通请求
case request: RequestChannel.Request =>
try {
request.requestDequeueTimeNanos = endTime
trace(s"Kafka request handler $id on broker $brokerId handling request $request")
// 调用KafkaApi.handle(),将请求交付给业务
apis.handle(request)
} catch {
case e: FatalExitError =>
shutdownComplete.countDown()
Exit.exit(e.statusCode)
case e: Throwable => error("Exception when handling request", e)
} finally {
// 释放请求对象占用的内存缓冲区资源
request.releaseBuffer()
}
case null => // continue
}
}
shutdownComplete.countDown()
}
}
KafkaController
KafkaController.startup中为每一个server都会启动一个eventManager。kafka集群中央控制器选举,leader选举,副本分配。
object KafkaController extends Logging {
def startup() = {
zkClient.registerStateChangeHandler(new StateChangeHandler {
override val name: String = StateChangeHandlers.ControllerHandler
override def afterInitializingSession(): Unit = {
eventManager.put(RegisterBrokerAndReelect)
}
override def beforeInitializingSession(): Unit = {
val queuedEvent = eventManager.clearAndPut(Expire)
// Block initialization of the new session until the expiration event is being handled,
// which ensures that all pending events have been processed before creating the new session
queuedEvent.awaitProcessing()
}
})
eventManager.put(Startup)
eventManager.start()
}
}
ReplicaManager
Kafka 中需要副本写入的场景主要有
- 生产者向 Leader 副本写入消息
- Follower 副本拉取消息后写入副本
- 消费者组写入组信息
- 事务管理器写入事务信息(包括事务标记、事务元数据等)
启动ISR线程
/* start replica manager */
replicaManager = createReplicaManager(isShuttingDown)
replicaManager.startup()
- -1: Partition Leader接收到消息之后,还必须要求ISR列表里跟Leader保持同步的那些Follower都要把消息同步过去,才能认为这条消息是写入成功了 如果说Partition Leader刚接收到了消息,但是结果Follower没有收到消息,此时Leader宕机了,那么客户端会感知到这个消息没发送成功,他会重试再次发送消息过去。 此时可能Partition 2的Follower变成Leader了,此时ISR列表里只有最新的这个Follower转变成的Leader了,那么只要这个新的Leader接收消息就算成功了 acks=all就代表数据一定不会丢失了吗? 当然不是,如果你的Partition只有一个副本,也就是一个Leader,任何Follower都没有,你认为acks=all有用吗? 当然没用了,因为ISR里就一个Leader,他接收完消息后宕机,也会导致数据丢失。 所以说,这个acks=all,必须跟ISR列表里至少有2个以上的副本配合使用,起码是有一个Leader和一个Follower才可以。 这样才能保证说写一条数据过去,一定是2个以上的副本都收到了才算是成功,此时任何一个副本宕机,不会导致数据丢失
- 1: 只要Partition Leader接收到消息而且写入本地磁盘了,就认为成功了,不管其他的Follower有没有同步过去这条消息了 这种设置其实是kafka默认的设置方式 也就是说默认情况下,要是不设置这个参数,只要Partition Leader写成功就算成功。 但是这里有一个问题,万一Partition Leader刚刚接收到消息,Follower还没来得及同步过去,结果Leader所在的broker宕机了,此时也会导致这条消息丢失,因为人家客户端已经认为发送成功了。
- 0: kafkaProducer在客户端,只要把消息发送出去,不管那条数据有没有在哪怕Partition Leader上落到磁盘,就不管他了,直接认为这个消息发送成功
class ReplicaManager() {
/**
* Append messages to leader replicas of the partition, and wait for them to be replicated to other replicas;
* the callback function will be triggered either when timeout or the required acks are satisfied;
* if the callback function itself is already synchronized on some object then pass this object to avoid deadlock.
*/
def appendRecords(timeout: Long, // 请求处理超时时间
requiredAcks: Short, // 请求acks 设置
internalTopicsAllowed: Boolean, // 是否允许写入内部Topic
origin: AppendOrigin, // 是否来自客户端
entriesPerPartition: Map[TopicPartition, MemoryRecords], // 待写入消息
responseCallback: Map[TopicPartition, PartitionResponse] => Unit, // 回调逻辑
delayedProduceLock: Option[Lock] = None,
recordConversionStatsCallback: Map[TopicPartition, RecordConversionStats] => Unit = _ => ()): Unit = {
// 合法取值是-1,0,1,否则视为非法
if (isValidRequiredAcks(requiredAcks)) {
val sTime = time.milliseconds
// 将消息追加到本地副本日志中
val localProduceResults = appendToLocalLog(internalTopicsAllowed = internalTopicsAllowed,
origin, entriesPerPartition, requiredAcks)
debug("Produce to local log in %d ms".format(time.milliseconds - sTime))
val produceStatus = localProduceResults.map { case (topicPartition, result) =>
topicPartition ->
ProducePartitionStatus(
// 设置下一条待写入消息的位移值
result.info.lastOffset + 1, // required offset
// 构建PartitionResponse封装写入结果
new PartitionResponse(result.error, result.info.firstOffset.getOrElse(-1), result.info.logAppendTime,
result.info.logStartOffset, result.info.recordErrors.asJava, result.info.errorMessage)) // response status
}
// 尝试更新消息格式转换的指标数据
recordConversionStatsCallback(localProduceResults.map { case (k, v) => k -> v.info.recordConversionStats })
// 用于判断消息集合被写入到日志之后,是否需要等待其他副本也写入成功
if (delayedProduceRequestRequired(requiredAcks, entriesPerPartition, localProduceResults)) {
// create delayed produce operation
val produceMetadata = ProduceMetadata(requiredAcks, produceStatus)
// 创建DelayedProduce延时请求对象,等待其他副本写入成功
val delayedProduce = new DelayedProduce(timeout, produceMetadata, this, responseCallback, delayedProduceLock)
// create a list of (topic, partition) pairs to use as keys for this delayed produce operation
val producerRequestKeys = entriesPerPartition.keys.map(TopicPartitionOperationKey(_)).toSeq
// try to complete the request immediately, otherwise put it into the purgatory
// this is because while the delayed produce operation is being created, new
// requests may arrive and hence make this operation completable.
// 再一次尝试完成该延时请求
// 如果暂时无法完成,则将对象放入到相应的Purgatory中等待后续处理
delayedProducePurgatory.tryCompleteElseWatch(delayedProduce, producerRequestKeys)
} else {
// we can respond immediately
// 无需等待其他副本写入完成,可以立即发送Response
val produceResponseStatus = produceStatus.map { case (k, status) => k -> status.responseStatus }
// 调用回调逻辑然后返回即可
responseCallback(produceResponseStatus)
}
} else {
// If required.acks is outside accepted range, something is wrong with the client
// Just return an error and don't handle the request at all
val responseStatus = entriesPerPartition.map { case (topicPartition, _) =>
topicPartition -> new PartitionResponse(Errors.INVALID_REQUIRED_ACKS,
LogAppendInfo.UnknownLogAppendInfo.firstOffset.getOrElse(-1), RecordBatch.NO_TIMESTAMP, LogAppendInfo.UnknownLogAppendInfo.logStartOffset)
}
// 构造INVALID_REQUIRED_ACKS 异常并封装进回调函数调用中
responseCallback(responseStatus)
}
}
/**
* Append the messages to the local replica logs
*/
private def appendToLocalLog(internalTopicsAllowed: Boolean,
origin: AppendOrigin,
entriesPerPartition: Map[TopicPartition, MemoryRecords],
requiredAcks: Short): Map[TopicPartition, LogAppendResult] = {
def processFailedRecord(topicPartition: TopicPartition, t: Throwable) = {
val logStartOffset = getPartition(topicPartition) match {
case HostedPartition.Online(partition) => partition.logStartOffset
case HostedPartition.None | HostedPartition.Offline => -1L
}
brokerTopicStats.topicStats(topicPartition.topic).failedProduceRequestRate.mark()
brokerTopicStats.allTopicsStats.failedProduceRequestRate.mark()
error(s"Error processing append operation on partition $topicPartition", t)
logStartOffset
}
// 遍历处理每个 topic 分区及其待追加的消息数据
trace(s"Append [$entriesPerPartition] to local log")
entriesPerPartition.map { case (topicPartition, records) =>
brokerTopicStats.topicStats(topicPartition.topic).totalProduceRequestRate.mark()
brokerTopicStats.allTopicsStats.totalProduceRequestRate.mark()
// reject appending to internal topics if it is not allowed
if (Topic.isInternal(topicPartition.topic) && !internalTopicsAllowed) {
(topicPartition, LogAppendResult(
LogAppendInfo.UnknownLogAppendInfo,
Some(new InvalidTopicException(s"Cannot append to internal topic ${topicPartition.topic}"))))
} else {
try {
// 获取分区对象
val partition = getPartitionOrException(topicPartition, expectLeader = true)
// 向该分区对象写入消息集合
val info = partition.appendRecordsToLeader(records, origin, requiredAcks)
val numAppendedMessages = info.numMessages
// update stats for successfully appended bytes and messages as bytesInRate and messageInRate
brokerTopicStats.topicStats(topicPartition.topic).bytesInRate.mark(records.sizeInBytes)
brokerTopicStats.allTopicsStats.bytesInRate.mark(records.sizeInBytes)
brokerTopicStats.topicStats(topicPartition.topic).messagesInRate.mark(numAppendedMessages)
brokerTopicStats.allTopicsStats.messagesInRate.mark(numAppendedMessages)
trace(s"${records.sizeInBytes} written to log $topicPartition beginning at offset " +
s"${info.firstOffset.getOrElse(-1)} and ending at offset ${info.lastOffset}")
(topicPartition, LogAppendResult(info))
} catch {
// NOTE: Failed produce requests metric is not incremented for known exceptions
// it is supposed to indicate un-expected failures of a broker in handling a produce request
case e@ (_: UnknownTopicOrPartitionException |
_: NotLeaderForPartitionException |
_: RecordTooLargeException |
_: RecordBatchTooLargeException |
_: CorruptRecordException |
_: KafkaStorageException) =>
(topicPartition, LogAppendResult(LogAppendInfo.UnknownLogAppendInfo, Some(e)))
case rve: RecordValidationException =>
val logStartOffset = processFailedRecord(topicPartition, rve.invalidException)
val recordErrors = rve.recordErrors
(topicPartition, LogAppendResult(LogAppendInfo.unknownLogAppendInfoWithAdditionalInfo(
logStartOffset, recordErrors, rve.invalidException.getMessage), Some(rve.invalidException)))
case t: Throwable =>
val logStartOffset = processFailedRecord(topicPartition, t)
(topicPartition, LogAppendResult(LogAppendInfo.unknownLogAppendInfoWithLogStartOffset(logStartOffset), Some(t)))
}
}
}
}
}
Partition
class Partition() {
def appendRecordsToLeader(records: MemoryRecords, origin: AppendOrigin, requiredAcks: Int): LogAppendInfo = {
// inReadLock是一个柯里化函数,第二个参数是一个函数,返回值是LogAppendInfo和HW是否增加的bool值
// 相当于给方法加了读锁
val (info, leaderHWIncremented) = inReadLock(leaderIsrUpdateLock) {
// leaderReplicaIfLocal表示本地broker中的leader副本
leaderLogIfLocal match {
case Some(leaderLog) =>
val minIsr = leaderLog.config.minInSyncReplicas
val inSyncSize = inSyncReplicaIds.size
// Avoid writing to leader if there are not enough insync replicas to make it safe
// 如果没有足够isr副本就返回异常,min.insync.replicas是和ack=-1一起使用的
if (inSyncSize < minIsr && requiredAcks == -1) {
throw new NotEnoughReplicasException(s"The size of the current ISR $inSyncReplicaIds " +
s"is insufficient to satisfy the min.isr requirement of $minIsr for partition $topicPartition")
}
// 只写入leaderlog
val info = leaderLog.appendAsLeader(records, leaderEpoch = this.leaderEpoch, origin,
interBrokerProtocolVersion)
// 写入完消息,尝试触发Fetch请求,比如满足消费者的fetch.max.bytes
// we may need to increment high watermark since ISR could be down to 1
(info, maybeIncrementLeaderHW(leaderLog))
case None =>
throw new NotLeaderForPartitionException("Leader not local for partition %s on broker %d"
.format(topicPartition, localBrokerId))
}
}
// some delayed operations may be unblocked after HW changed
if (leaderHWIncremented)
tryCompleteDelayedRequests()
else {
// probably unblock some follower fetch requests since log end offset has been updated
delayedOperations.checkAndCompleteFetch()
}
info
}
}
Log
class Log()
def appendAsLeader(records: MemoryRecords,
leaderEpoch: Int,
origin: AppendOrigin = AppendOrigin.Client,
interBrokerProtocolVersion: ApiVersion = ApiVersion.latestVersion): LogAppendInfo = {
append(records, origin, interBrokerProtocolVersion, assignOffsets = true, leaderEpoch)
}
private def append(records: MemoryRecords,
origin: AppendOrigin,
interBrokerProtocolVersion: ApiVersion,
assignOffsets: Boolean,
leaderEpoch: Int): LogAppendInfo = {
maybeHandleIOException(s"Error while appending records to $topicPartition in dir ${dir.getParent}") {
val appendInfo = analyzeAndValidateRecords(records, origin)
// return if we have no valid messages or if this is a duplicate of the last appended entry
if (appendInfo.shallowCount == 0)
return appendInfo
// trim any invalid bytes or partial messages before appending it to the on-disk log
var validRecords = trimInvalidBytes(records, appendInfo)
// they are valid, insert them in the log
lock synchronized {
checkIfMemoryMappedBufferClosed()
if (assignOffsets) {
// assign offsets to the message set
val offset = new LongRef(nextOffsetMetadata.messageOffset)
appendInfo.firstOffset = Some(offset.value)
val now = time.milliseconds
// 各种验证
val validateAndOffsetAssignResult = try {
LogValidator.validateMessagesAndAssignOffsets(validRecords,
topicPartition,
offset,
time,
now,
appendInfo.sourceCodec,
appendInfo.targetCodec,
config.compact,
config.messageFormatVersion.recordVersion.value,
config.messageTimestampType,
config.messageTimestampDifferenceMaxMs,
leaderEpoch,
origin,
interBrokerProtocolVersion,
brokerTopicStats)
} catch {
case e: IOException =>
throw new KafkaException(s"Error validating messages while appending to log $name", e)
}
// 验证通过后的消息
validRecords = validateAndOffsetAssignResult.validatedRecords
// 根据校验结果完善appendInfo对象
appendInfo.maxTimestamp = validateAndOffsetAssignResult.maxTimestamp
appendInfo.offsetOfMaxTimestamp = validateAndOffsetAssignResult.shallowOffsetOfMaxTimestamp
appendInfo.lastOffset = offset.value - 1
appendInfo.recordConversionStats = validateAndOffsetAssignResult.recordConversionStats
if (config.messageTimestampType == TimestampType.LOG_APPEND_TIME)
appendInfo.logAppendTime = now
// re-validate message sizes if there's a possibility that they have changed (due to re-compression or message
// format conversion)
if (validateAndOffsetAssignResult.messageSizeMaybeChanged) {
for (batch <- validRecords.batches.asScala) {
if (batch.sizeInBytes > config.maxMessageSize) {
// we record the original message set size instead of the trimmed size
// to be consistent with pre-compression bytesRejectedRate recording
brokerTopicStats.topicStats(topicPartition.topic).bytesRejectedRate.mark(records.sizeInBytes)
brokerTopicStats.allTopicsStats.bytesRejectedRate.mark(records.sizeInBytes)
throw new RecordTooLargeException(s"Message batch size is ${batch.sizeInBytes} bytes in append to" +
s"partition $topicPartition which exceeds the maximum configured size of ${config.maxMessageSize}.")
}
}
}
} else {
// we are taking the offsets we are given
if (!appendInfo.offsetsMonotonic)
throw new OffsetsOutOfOrderException(s"Out of order offsets found in append to $topicPartition: " +
records.records.asScala.map(_.offset))
if (appendInfo.firstOrLastOffsetOfFirstBatch < nextOffsetMetadata.messageOffset) {
// we may still be able to recover if the log is empty
// one example: fetching from log start offset on the leader which is not batch aligned,
// which may happen as a result of AdminClient#deleteRecords()
val firstOffset = appendInfo.firstOffset match {
case Some(offset) => offset
case None => records.batches.asScala.head.baseOffset()
}
val firstOrLast = if (appendInfo.firstOffset.isDefined) "First offset" else "Last offset of the first batch"
throw new UnexpectedAppendOffsetException(
s"Unexpected offset in append to $topicPartition. $firstOrLast " +
s"${appendInfo.firstOrLastOffsetOfFirstBatch} is less than the next offset ${nextOffsetMetadata.messageOffset}. " +
s"First 10 offsets in append: ${records.records.asScala.take(10).map(_.offset)}, last offset in" +
s" append: ${appendInfo.lastOffset}. Log start offset = $logStartOffset",
firstOffset, appendInfo.lastOffset)
}
}
// update the epoch cache with the epoch stamped onto the message by the leader
validRecords.batches.asScala.foreach { batch =>
if (batch.magic >= RecordBatch.MAGIC_VALUE_V2) {
maybeAssignEpochStartOffset(batch.partitionLeaderEpoch, batch.baseOffset)
} else {
// In partial upgrade scenarios, we may get a temporary regression to the message format. In
// order to ensure the safety of leader election, we clear the epoch cache so that we revert
// to truncation by high watermark after the next leader election.
leaderEpochCache.filter(_.nonEmpty).foreach { cache =>
warn(s"Clearing leader epoch cache after unexpected append with message format v${batch.magic}")
cache.clearAndFlush()
}
}
}
// Records总消息不能比segment.bytes大
// check messages set size may be exceed config.segmentSize
if (validRecords.sizeInBytes > config.segmentSize) {
throw new RecordBatchTooLargeException(s"Message batch size is ${validRecords.sizeInBytes} bytes in append " +
s"to partition $topicPartition, which exceeds the maximum configured segment size of ${config.segmentSize}.")
}
// 是否需要生成一个新的segment,具体判断条件见下文
// maybe roll the log if this segment is full
val segment = maybeRoll(validRecords.sizeInBytes, appendInfo)
// 保存位移的VO
val logOffsetMetadata = LogOffsetMetadata(
messageOffset = appendInfo.firstOrLastOffsetOfFirstBatch,
segmentBaseOffset = segment.baseOffset,
relativePositionInSegment = segment.size)
// now that we have valid records, offsets assigned, and timestamps updated, we need to
// validate the idempotent/transactional state of the producers and collect some metadata
val (updatedProducers, completedTxns, maybeDuplicate) = analyzeAndValidateProducerState(
logOffsetMetadata, validRecords, origin)
maybeDuplicate.foreach { duplicate =>
appendInfo.firstOffset = Some(duplicate.firstOffset)
appendInfo.lastOffset = duplicate.lastOffset
appendInfo.logAppendTime = duplicate.timestamp
appendInfo.logStartOffset = logStartOffset
return appendInfo
}
// 真正append日志的是LogSegment对象
segment.append(largestOffset = appendInfo.lastOffset,
largestTimestamp = appendInfo.maxTimestamp,
shallowOffsetOfMaxTimestamp = appendInfo.offsetOfMaxTimestamp,
records = validRecords)
// Increment the log end offset. We do this immediately after the append because a
// write to the transaction index below may fail and we want to ensure that the offsets
// of future appends still grow monotonically. The resulting transaction index inconsistency
// will be cleaned up after the log directory is recovered. Note that the end offset of the
// ProducerStateManager will not be updated and the last stable offset will not advance
// if the append to the transaction index fails.
// 更新LEO,lastOffset + 1
updateLogEndOffset(appendInfo.lastOffset + 1)
// update the producer state
for (producerAppendInfo <- updatedProducers.values) {
producerStateManager.update(producerAppendInfo)
}
// update the transaction index with the true last stable offset. The last offset visible
// to consumers using READ_COMMITTED will be limited by this value and the high watermark.
for (completedTxn <- completedTxns) {
val lastStableOffset = producerStateManager.lastStableOffset(completedTxn)
segment.updateTxnIndex(completedTxn, lastStableOffset)
producerStateManager.completeTxn(completedTxn)
}
// always update the last producer id map offset so that the snapshot reflects the current offset
// even if there isn't any idempotent data being written
producerStateManager.updateMapEndOffset(appendInfo.lastOffset + 1)
// update the first unstable offset (which is used to compute LSO)
maybeIncrementFirstUnstableOffset()
trace(s"Appended message set with last offset: ${appendInfo.lastOffset}, " +
s"first offset: ${appendInfo.firstOffset}, " +
s"next offset: ${nextOffsetMetadata.messageOffset}, " +
s"and messages: $validRecords")
if (unflushedMessages >= config.flushInterval)
flush()
appendInfo
}
}
}
}
GroupCoordinator
GroupCoordinator处理组成员管理和offset管理,每个kafka服务器初始化一个协作器来负责一系列组别。每组基于它们的组名来赋予协作器。
groupCoordinator = GroupCoordinator(config, zkClient, replicaManager, Time.SYSTEM, metrics)
groupCoordinator.startup()
__consumer_offsets topic,它是 Kafka 内部使用的一个 topic,专门用来存储 group 消费的情况,默认情况下有50个 partition,每个 partition 默认有三个副本,而具体的一个 group 的消费情况要存储到哪一个 partition 上,是根据 abs(GroupId.hashCode()) % NumPartitions 来计算的(其中,NumPartitions 是 __consumer_offsets 的 partition 数,默认是50个)
其他
https://my.oschina.net/keepal/blog/5273418
https://www.cnblogs.com/huxi2b/p/4534986.html
kafka源码阅读笔记
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45723348/article/details/115763570
kafka server源代码分析
https://www.cnblogs.com/huxi2b/p/4545613.html
Kafka 源码解析之Broker请求处理流程
https://www.jianshu.com/p/d0f4e1dc6bcf
Kafka 请求模块
https://blog.csdn.net/lianggx3/article/details/108700699
源码面前了无秘密【Kafka】:KafkaApis.handleProduceRequest
http://www.xumenger.com/4-kafka-apis-handleProduceRequest-20210519/